Figure 2.
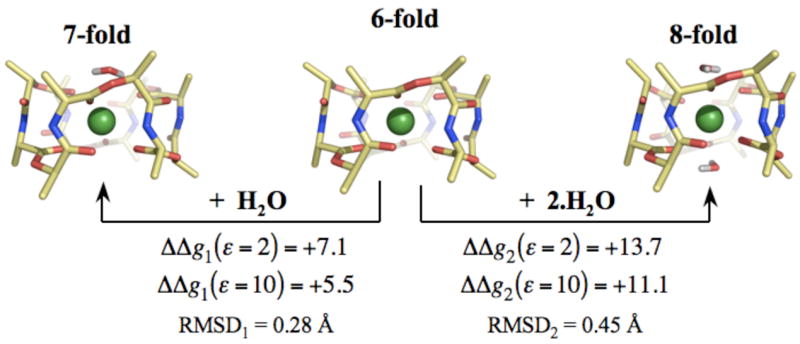
Structural and energetic changes associated with increasing the coordination of K+ ions bound to valinomycin. K+ ions complexed to valinomycin are in direct coordination with 6 carbonyl ligands. Increasing their coordination to 7 and 8 using n=1 and n=2 water molecules destabilizes the K+ complex. ΔΔgn(ε) denotes this change in complexation energy, as determined from the reaction given by equation 3. ΔΔgn(ε) are provided for two different values of ε, which are representative of the dielectric constant of the lipid membranes. Note that calculations using higher values of ε, such as ε=80, also result in a greater stability of the 6-fold coordination. RMSDn reflects the change in the backbone structure of K+ bound valinomycin due to complexation by n water molecules.
