Figure 1. The structure of NotI restriction endonuclease.
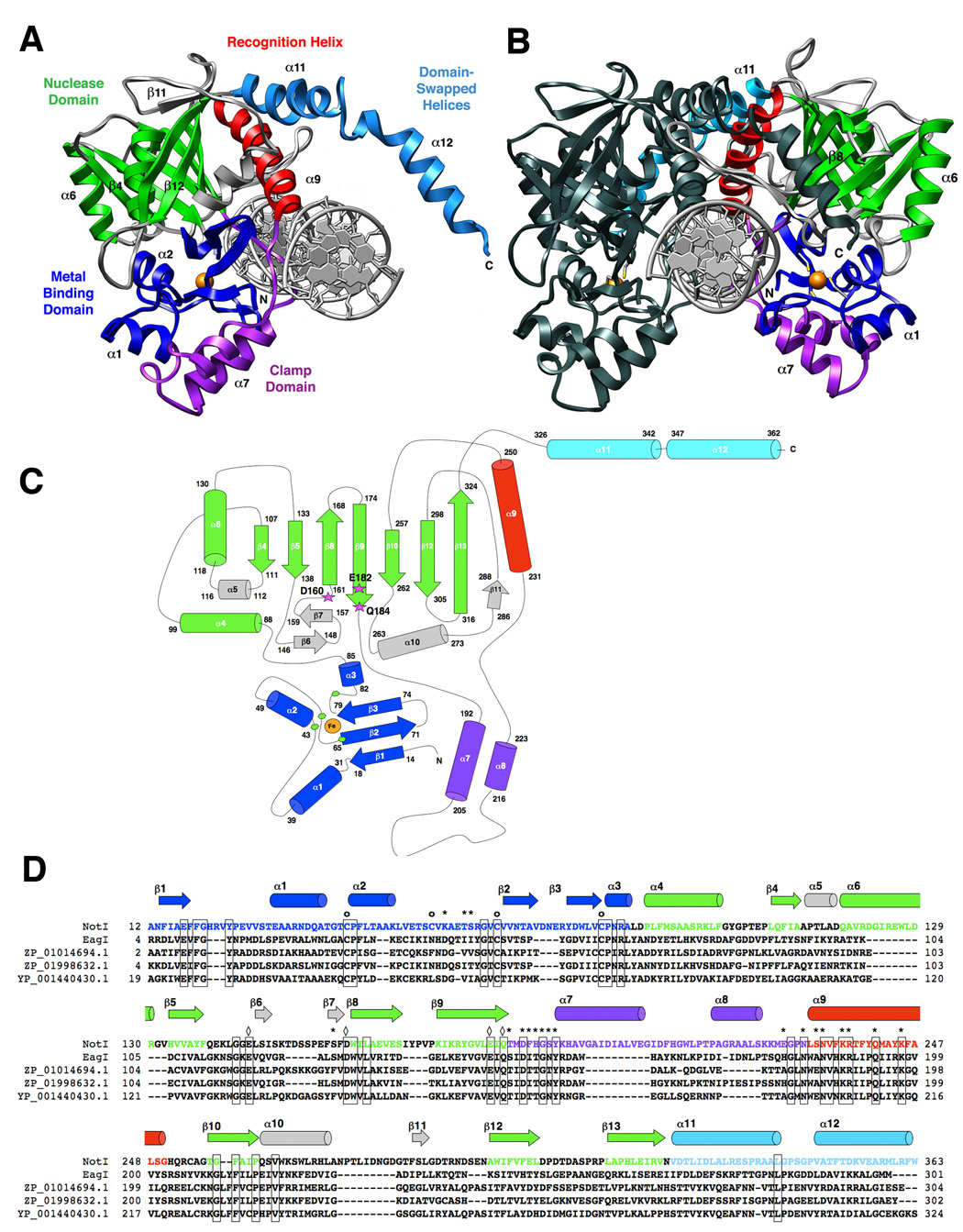
The protein is colored according to individual structural domains and motifs; the same color scheme is used in all panels. The N-terminal 85 residues (blue) form a unique metal-binding domain that uses a four-cysteine coordination scheme; this domain is followed by the PD…D/E-xK catalytic domain (green). An elaboration on this fold, extending from between two β-stands, presents a two-helix bundle “clamp” domain (purple) that wraps around the metal-bound domain. This region, along with an adjacent recognition helix (red) contributes the majority of direct contacts between the protein and bound DNA. Finally, two helices extend from the C-terminal end of the protein and form a domain-swapped dimerization motif (cyan). Additional structural elaborations on the nuclease core are colored gray. Panel A: A single monomer of NotI with the full-length (22bp) palindromic DNA target site. The bound iron ion is shown as an orange sphere, and select secondary structural elements are labeled by number for reference. Panel B: The homodimeric endonuclease bound to its cognate DNA target site. One subunit is colored as described above (the opposite protein chain colored relative to panel a); the second subunit is colored uniformly dark for clarity and contrast. The cysteine sidechains of the Fe-Cys4 iron-binding motif are shown as sticks and colored by element. Panel C: Topology of the NotI protein fold. Residues at boundaries of secondary structural elements are numbered; active site residues are indicated with magenta stars and bold labels; The bound iron is shown as an orange circle, and iron ligands (Cys 42, 55, 65, and 81) are represented by green hexagons. Individual secondary structural elements are numbered in sequential order. Panel D: Sequence homology between NotI, EagI (GenBank EU 371940, which recognizes and cuts a six-base site corresponding to the central six positions of the 8-base NotI target site), and homologues ZP_01014694.1 from Rhodobacterales bacterium HTCC2654, ZP_01998632.1 from Beggiatoa sp. PS, and YP_001440430.1 from Enterobacter sakazakii ATCC BAA_894. Iron-binding residues (of which three out of four are conserved in EagI) are indicated with circles (o); DNA-binding residues (of which ten out of nineteen are conserved in EagI) are indicated with asterisks (*); and catalytic residues of the PD…(D/E)xK endonuclease motif (two-metal ion mechanism) are indicated with diamonds (◊) (all are conserved).
