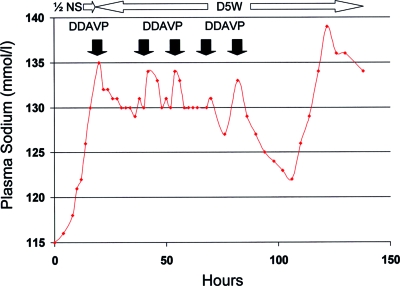
Figure 1.
Patient 2, who presented with delirium as a result of a plasma sodium concentration (PNa) of 115 mmol/L and alcohol withdrawal, was given multiple doses of desmopressin acetate (DDAVP; filled arrows) in the intensive care unit after a spontaneous water diuresis had increased her PNa by 20 mmol/L over 21 h despite infusion of 0.45% saline (1/2 NS) at 150 ml/h. The final dose of DDAVP was given just before transfer from the intensive care unit, and it was followed by excessive re-lowering of the PNa because of the unintentional continuation of 5% dextrose in water (D5W). After the PNa had fallen from 133 to 122 mmol/L over 24 h (with no worsening of the patient's neurologic condition), a final water diuresis emerged, increasing the PNa to 138 over 17 h despite continued infusion of D5W at 150 ml/h without DDAVP.