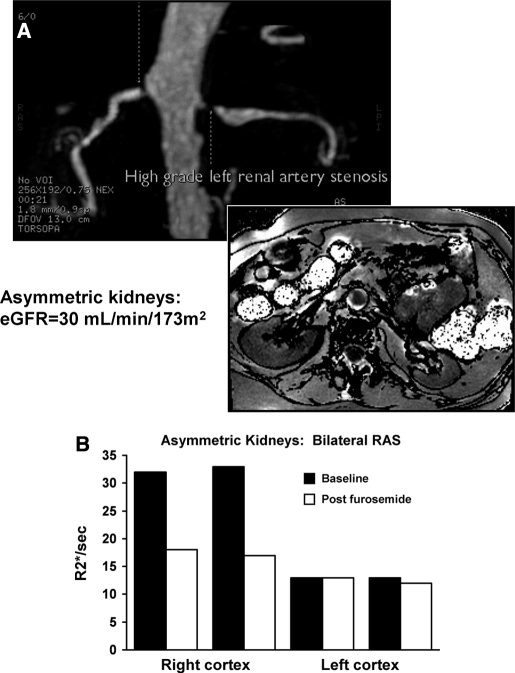
Figure 5.
MR angiogram in a patient with bilateral renal arterial stenosis (A), more severe on the left, on the basis of poststenotic dilation and reduced parenchymal volume. BOLD imaging demonstrated low levels of R2* both before and after furosemide (B). The right kidney had normal volume with higher baseline R2* with a large fall in R2* after administration of furosemide. These data suggest higher deoxyhemoglobin levels in the right kidney with exaggerated furosemide-suppressible oxygen consumption.