Figure 5.
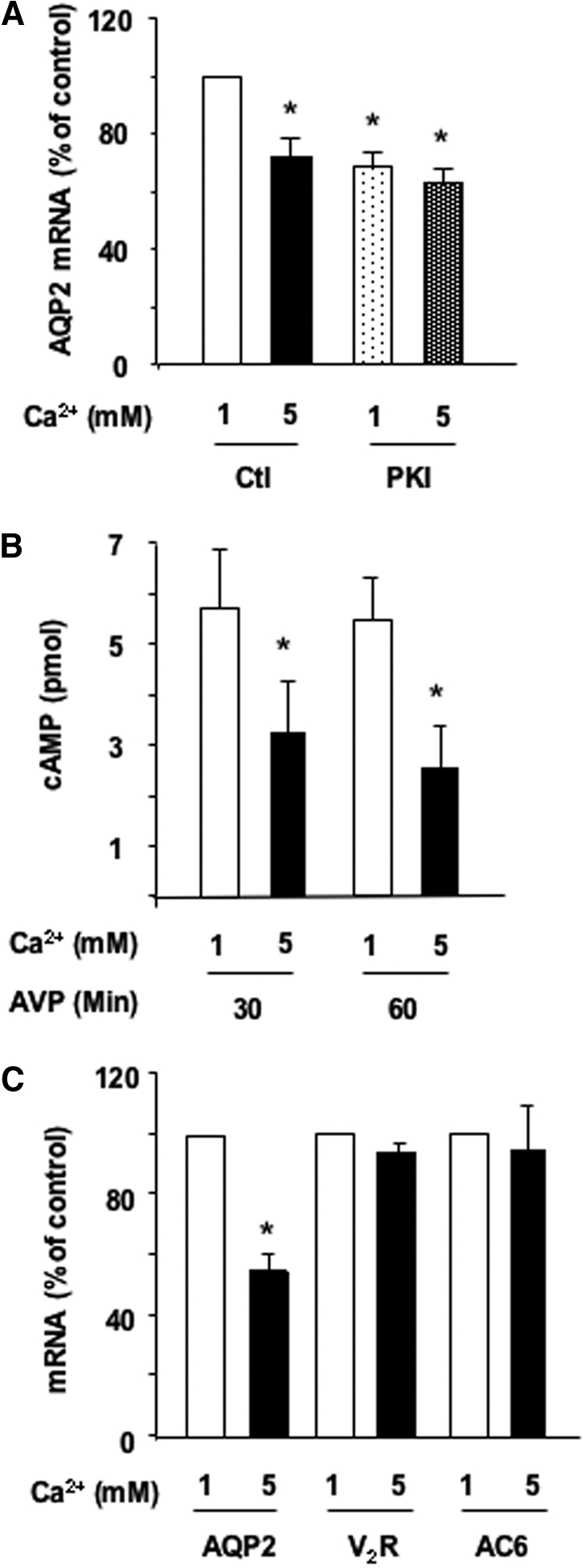
Role of the cAMP-PKA pathway in the calcium-induced attenuation of AVP-dependent AQP2 expression. (A) Confluent mpkCCDcl4 cells grown on filters in culture medium containing baseline (1 mM) calcium were preincubated for 24 h at 37°C with 10−9 M AVP. Cells were then incubated for another 24 h in the continuous presence of AVP and in the presence of 1 or 5 mM apical calcium and treated or not with 5 × 10−6 M myristoylated PKA inhibitor (PKI). After RNA extraction, real-time PCR was performed as described in the Concise Methods section using primers against AQP2. Results are expressed as a percentage of control values determined after 24 h of incubation in the presence of 1 mM calcium (100%). Bars are means ± SEM from four independent experiments. (B) Confluent mpkCCDcl4 cells grown on filters were preincubated for 24 h at 37°C in the presence of 1 or 5 mM apical calcium and treated or not for 30 to 60 min with 10−9 M AVP. Cellular cAMP content was determined as described in the Concise Methods section. Results are expressed as pmol cAMP × 106 cells−1 and are means ± SEM from five independent experiments. (C) Cells were treated as in A before RNA extraction. Real-time PCR was performed as described in the Concise Methods section using primers against AQP2, the vasopressin V2 receptor (V2R), or type 6 AC (AC6). Results are expressed as a percentage of control values determined after 24 h of incubation in the presence of 1 mM calcium (100%). Bars are means ± SEM from four independent experiments. *P < 0.05.
