Figure 3.
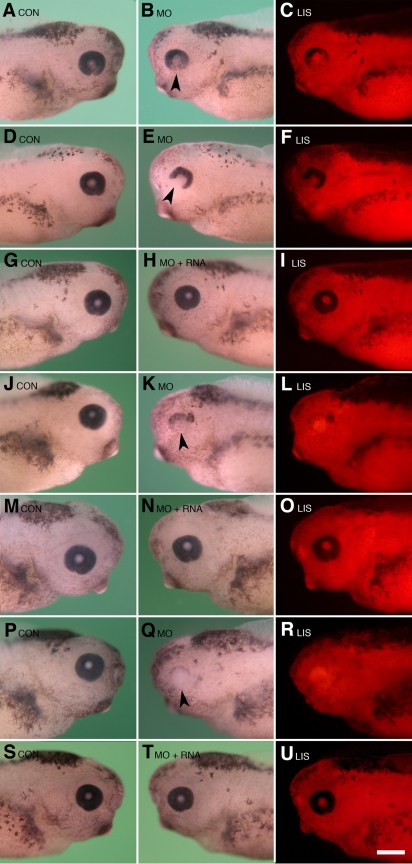
Results of Psf2 morpholino knockdown and RNA rescue experiments. Dorsal is toward the top in each figure. A-F: Typical eye defects observed following unilateral injection of lissamine-tagged Psf2MO into single blastomeres at the two-cell stage (equivalent to 2.25 ng/cell at the eight-cell stage) are shown. A: Normal control (uninjected, CON) side is shown. This side is the normal part the embryo shown in B-C. B: Minor eye defect is observed on the Psf2MO-injected side (opposite that shown in A) as indicated by arrow. Note the slight decrease in retinal pigmentation in the ventral region and the reduced size of the optic cup compared to that shown in A. C: Corresponding fluorescence image to that shown in B, the image shows the distribution of the lissamine-tagged morpholino (LIS). D: Normal control, uninjected side is shown. This side is the normal part of the embryo shown in E-F. E: A severe eye defect phenotype is observed following Psf2MO injection. Note the smaller size of the eye and severe reduction in the ventral region of the optic cup, denoted by the arrow in E. F: The corresponding fluorescence image shows the distribution of the lissamine-tagged morpholino for the embryo shown in E. G-I: The typical result observed following the co-injection of 2.25 ng Psf2 morpholino and 1000 pg synthetic altPsf2 RNA is shown. G: The normal control, uninjected side of the embryo shown in H-I is displayed. H: There was normal morphological development following the co-injection of Psf2MO (equivalent to 2.25 ng/blastomere at the eight-cell stage) and 1000 pg rescue RNA (altPsf2 RNA). I: The corresponding fluorescence image to that shown in H shows distribution of the lissamine-tagged morpholino. J-L: Typical severe eye defect is observed following the unilateral injection of lissamine-tagged Psf2MO into single blastomeres at the two-cell and four-cell stages (equivalent to 4.5 ng/blastomere at the eight-cell stage). J: The normal control, uninjected side of the embryo shown in K-L is pictured. K: Typical severe eye defect phenotype is observed following Psf2MO injection. Note the smaller size of the eye and severe reduction in the ventral region of the optic cup, denoted by the arrow in K. L: The corresponding fluorescence image shows the distribution of the lissamine-tagged morpholino for the embryo shown in K. M-O: The typical result is observed following the co-injection of 4.5 ng Psf2 morpholino and 1000 pg synthetic altPsf2 RNA. M: The normal control, uninjected side of the embryo shown in N-O is displayed. N: Normal morphological development is observed following the co-injection of Psf2MO (equivalent to 4.5 ng/blastomere at the eight-cell stage) and 1000 pg rescue RNA (altPsf2 RNA). O: The corresponding fluorescence image to that shown in N shows the distribution of the lissamine-tagged morpholino. P-R: Typical severe eye defect is observed following unilateral injection of lissamine-tagged Psf2MO into single blastomeres at the two-cell and four-cell stages (equivalent to 6 ng/blastomere at the eight-cell stage). P: The normal control, uninjected side of the embryo shown in Q and R is shown. Q: The typical severe eye defect phenotype is displayed following Psf2MO injection. Note the severe reduction in the ventral region of the optic cup, denoted by the arrow in Q, and the overall lack of retinal pigmentation. R: The corresponding fluorescence image shows the distribution of the lissamine-tagged morpholino for the embryo shown in Q. S-U: The typical result is observed following co-injection of 6 ng Psf2 morpholino and 1000 pg synthetic altPsf2 RNA. S: The normal control, uninjected side of the embryo shown in T-U is displayed. T: There is normal morphological development following the co-injection of Psf2MO (equivalent to 6 ng/blastomere at the eight-cell stage) and 1000 pg rescue RNA (altPsf2 RNA). U: The corresponding fluorescence image to that shown in S shows the distribution of the lissamine-tagged morpholino. The scale bar in U is equal to 450 µm.