Abstract
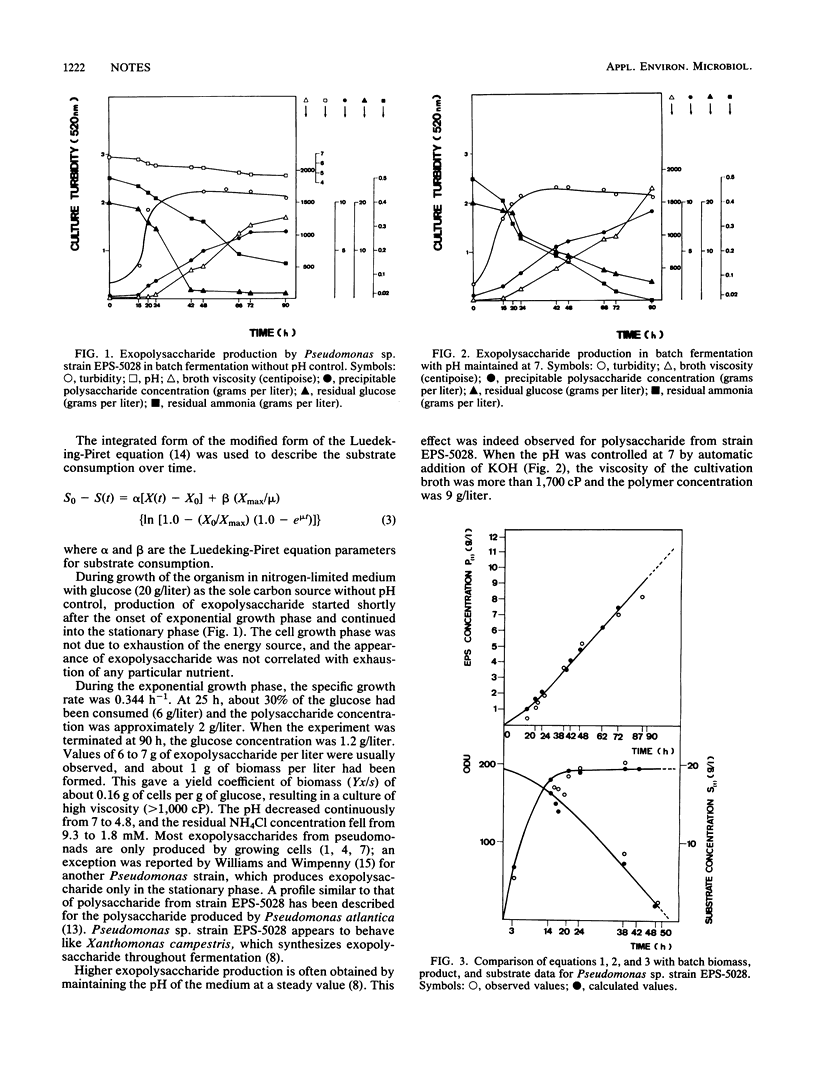
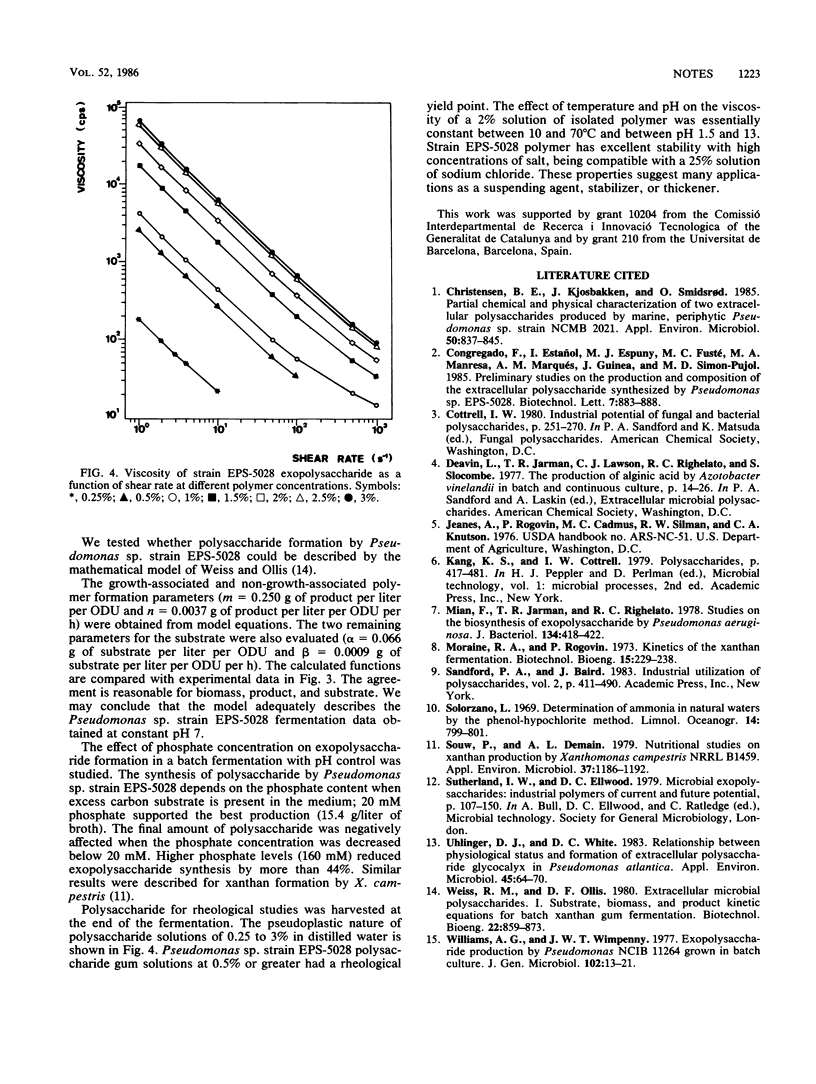
During batch aerobic submerged fermentation, the exopolysaccharide synthesis by Pseudomonas sp. strain EPS-5028 occurred in growth- and non-growth-linked processes. Polysaccharide formation increased when the pH was controlled at 7 during fermentation. Exopolysaccharide production depended on the phosphate content of the medium. The polymer exhibited a pseudoplastic nature, had good thermostability, and was affected neither by pH nor by high concentrations of salt.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christensen B. E., Kjosbakken J., Smidsrød O. Partial Chemical and Physical Characterization of Two Extracellular Polysaccharides Produced by Marine, Periphytic Pseudomonas sp. Strain NCMB 2021. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):837–845. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.837-845.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian F. A., Jarman T. R., Righelato R. C. Biosynthesis of exopolysaccharide by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):418–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.418-422.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souw P., Demain A. L. Nutritional Studies on Xanthan Production by Xanthomonas campestris NRRL B1459. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1186–1192. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1186-1192.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlinger D. J., White D. C. Relationship Between Physiological Status and Formation of Extracellular Polysaccharide Glycocalyx in Pseudomonas atlantica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.64-70.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. G., Wimpenny J. W. Exopolysaccharide production by Pseudomonas NCIB11264 grown in batch culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Sep;102(1):13–21. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


