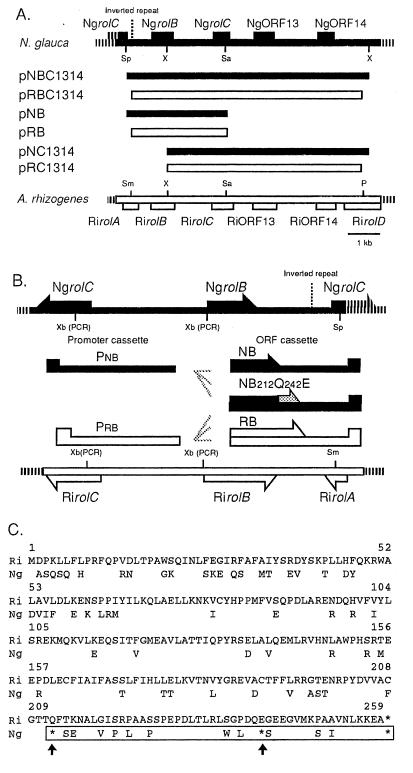
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of constructs. A restriction map of the NgrolB-NgORF14 region (Top, solid line) is compared with the RirolB-RiORF14 region (Bottom, open box). The various fragments and chimeric constructs are indicated by solid bars (Ngrol genes) and open boxes (Rirol genes). P, PvuI; Sa, SalI; Sm, SmaI; Sp, SpeI; X, XhoI. (B) Promoter and ORF cassettes. Pnb, NgrolB promoter cassette; Prb, RirolB promoter cassette; NB, cassette harboring the coding and 3′ untranslated region of NgrolB; NB212Q242E, NB cassette under the modifications of site-directed mutagenesis; RB, cassette harboring the coding and untranslated region of RirolB; Xb (PCR), new restriction sites for XbaI that were created by PCR. (C) Comparison of the amino acid sequences deduced from the RirolB and NgrolB genes (4, 11). Amino acids encoded by NgrolB that are the same as those encoded by RirolB are not shown. Asterisks indicate termination codons. Arrows indicate the termination codons that were changed by site-directed mutagenesis. The restored region in the amino acid sequence encoded by NgrolB212Q242E is indicated by a box.