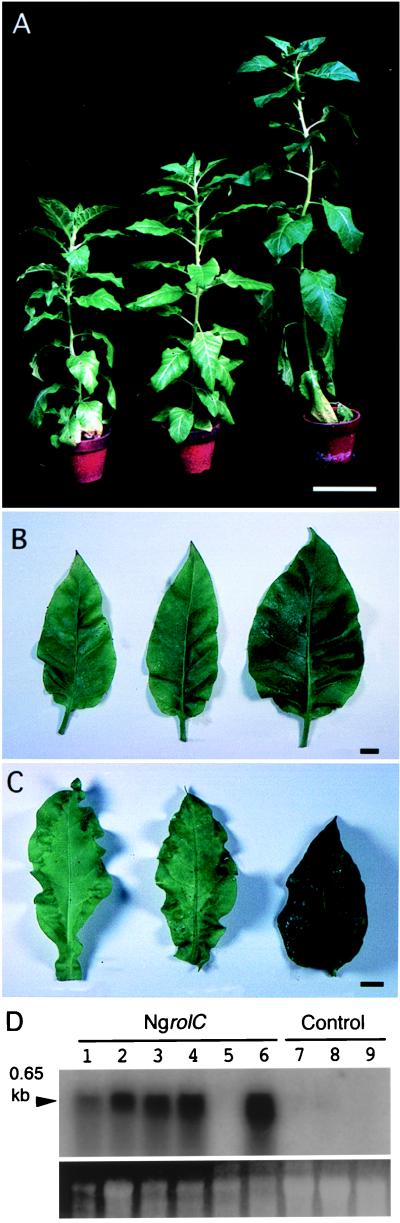
Figure 5.
Comparison of plants transformed with rolC homologues. (A) Whole plants harboring P35S-RirolC chimeric gene (Left) or P35S-NgrolC gene (Center) and a control plant (Right). Bar = 10 cm. (B) Leaves from transgenic plants harboring P35S-RirolC (Left) or P35S-NgrolC (Center) and from a control plant (Right). (C) Abnormal chimeric morphology of leaves from transgenic plants harboring P35S-RirolC gene (Left) or the P35S-NgrolC gene (Center). A normal leaf of wild-type tobacco is shown as a control (Right). (B and C) Bars = 1 cm. (D) Transcripts of the NgrolC in leaf tissues of transgenic plants. Lanes 1–5, T0 plants infected with A. tumefaciens harboring the P35S-NgrolC gene; lane 6, a T1 plant; lanes 7–9, wild-type and control tobacco plants. The probe was a 1.1-kbp EcoRV-EcoRI fragment of λNg31.