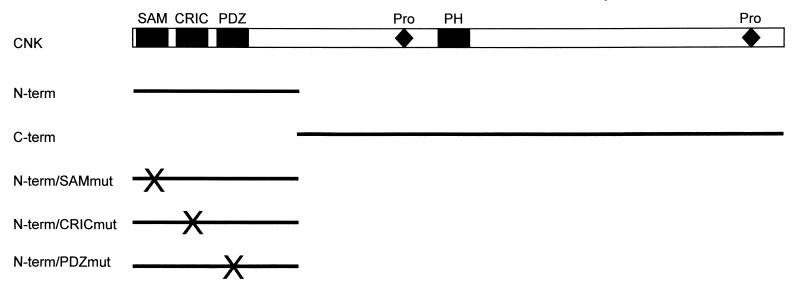
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the CNK constructs used in this study. CNK is 1,554 amino acids long and contains several domains that probably recognize other proteins: a sterile alpha motif (SAM) domain; a conserved region in CNK (CRIC) domain; a PSD-95, ZO-1/2, Dlg-1 (PDZ) domain; a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain; and two proline-rich (Pro) stretches that have consensus binding sites for SH3 domains. The regions present in the truncated CNK variants are denoted by a line, which corresponds to amino acids 2–384 for CNKN-term constructs (X schematically indicates the position of the mutant domains) and to amino acids 381–1,554 for CNKC-term. To disrupt the normal function of CNKN-term domains, conserved residues in the SAM and PDZ domains were changed by site-directed mutagenesis, whereas a mutation analogous to the one found in the cnkS-726 loss-of-function was introduced to generate a mutant CRIC domain. CNKN-termSAMmut has amino acids WI at positions 17 and 18 changed to SS. CNKN-termCRICmut has a deletion of amino acids AHR at position 162. CNKN-termPDZmut has amino acids GF at positions 217 and 218 changed to SS. All CNK constructs have an N-terminal FLAG epitope (MDYKDDDDK).