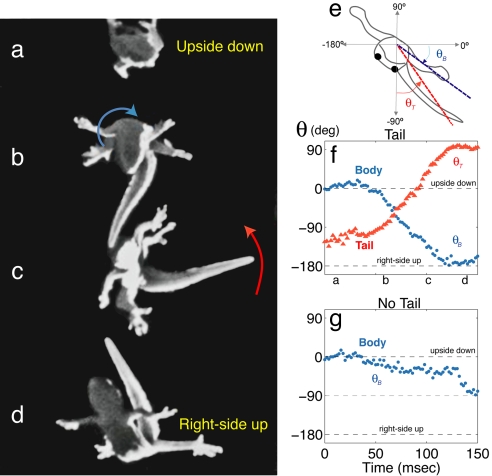
Fig. 3.
Tail-induced air-righting maneuver in geckos (SI Movie 4). (a) At takeoff the gecko released from an upside down (supine) posture. (b and c) Counterclockwise tail rotation (red arrow; θT) induced a clockwise rotation of the body (blue arrow; θB). (d) As the gecko's body attained right-side up (prone) posture, the tail stopped rotating. The animal maintained a skydiving posture during the subsequent free fall. (e) Schematic of a supine gecko falling to show angle convention. (f and g) Rotation of body and tail segments as a function of time in tailed (f) and tailless animals (g).