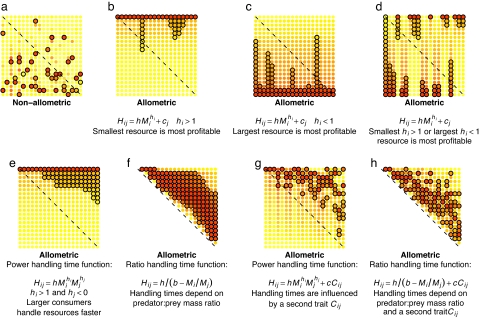
Fig. 1.
Food web structures illustrated in predation matrices show the importance of allometry for structure. The allometric equation is given below the panel; parameter values are arbitrary and do not affect the qualitative patterns illustrated. Black circles indicate a realized feeding interaction. Body size increases from left to right and top to bottom, so that interactions in the upper-right triangle are for consumers feeding on resources smaller than themselves. Dashed diagonals lines indicate the position that cannibalistic interactions would take. Each element of the predation matrix is colored according to resource (row) profitability for the consumer (column) (yellow to red indicate low to high profitability, Ei/Hij). In g and h, no color indicates zero profitability. In b, c, and d, variation in diet breadth is caused by the effect of consumer identity (cj) on handling times; here, this effect is independent of consumer size.