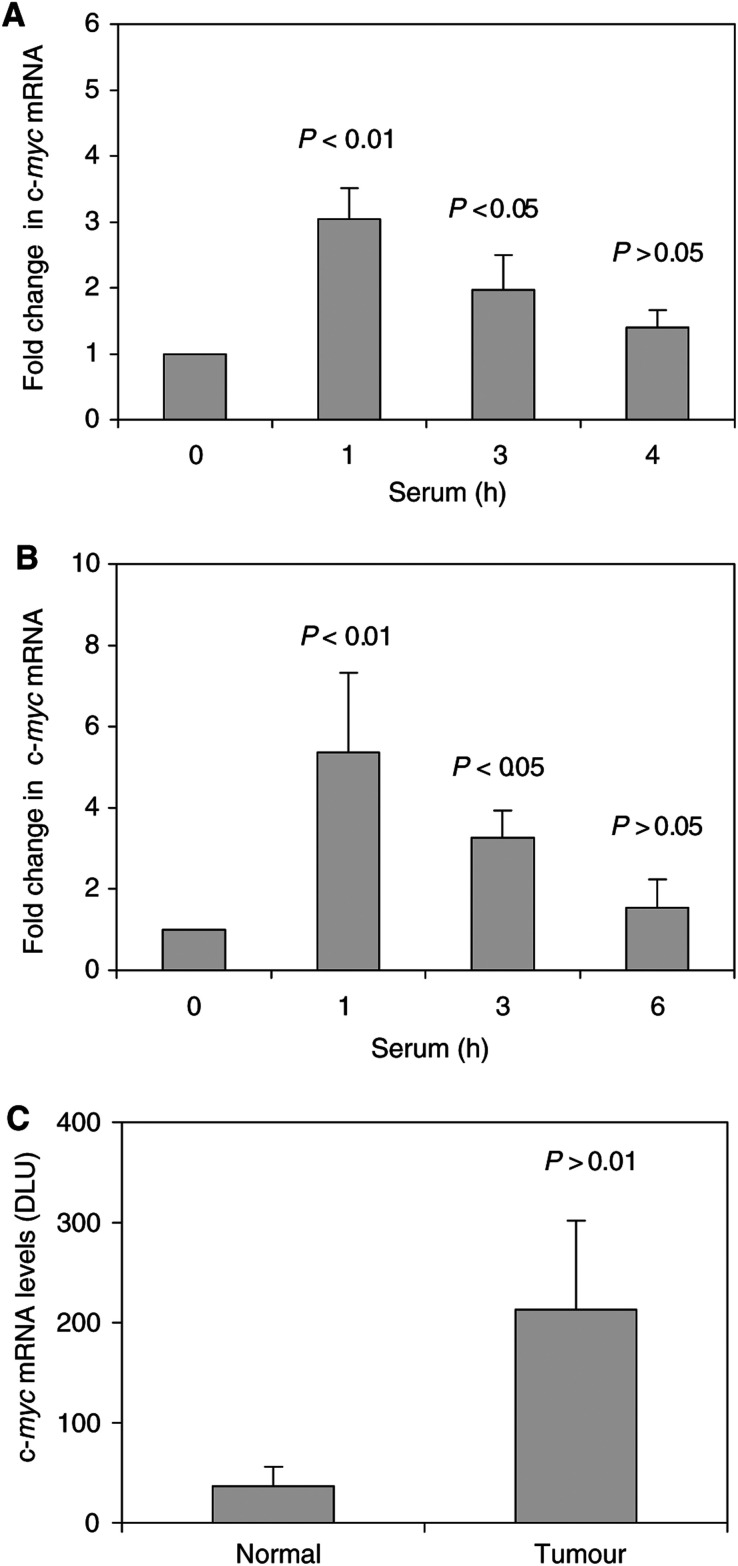
Figure 8.
c-myc mRNA transcript levels in serum-treated hepatocyte cultures (A), postpartial hepatectomy (B) and in hepatic tumours (C). (A) Serum-deprived HTC-IR cells were treated with 15% FBS for 0, 1, 3, 6 and 24 h. After harvesting the cells, total RNA was isolated and used in RT. PCR was carried out using [α32P]dCTP (0.5 μCi per reaction) and c-myc primers (forward: GCAAATGCTCCAGCCCCAGGTC; reverse: AGTCCCAAAGCCCCAGCCAAGGTT). PCR products were resolved by native PAGE and were quantified using a phosphorimager (Cyclone, Packard meriden, CT, USA). Results are expressed as fold increase in the mRNA level at each time point of serum treatment compared to the levels seen in untreated cells. The values represent means±s.d. (n=3). (B) Partial hepatectomy and control sham operation were carried out as in Figure 3. At given time points following surgery, the livers were harvested from each group and total RNA was isolated (three animals for each time point), c-myc mRNA levels were determined by RT–PCR as above. Results are expressed as fold increase in mRNA levels compared to sham-operated mice. (C) Comparison of c-myc mRNA levels in spontaneous hepatocellular carcinoma and the normal surrounding liver tissue, c-myc mRNA levels were determined by RT–PCR and the 32P signal of the labelled products is expressed in DLU. The results represent means±s.d. (n=5 animals).