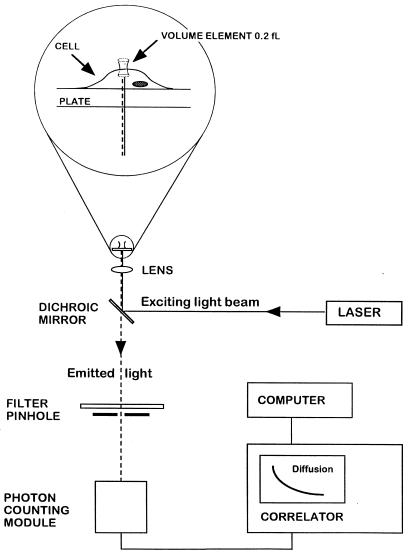
Figure 1.
FCS experimental setup. Light from an argon ion laser is focused by means of a dichroic mirror and a lens to form a small volume element (0.2 fl). The laser beam is projected from below into a well containing a monolayer of cultured cells and tetramethylrhodamine (Rh)-labeled ligand (see magnified diagram at the top). After excitation of the labeled ligand, emitted light is transmitted via the dichroic mirror, a bandpass filter, and a pinhole to a photodetector. The volume element is positioned onto the cell surface with a microscope for detection of ligand binding. The dimensions of the laser beam focus and the pinhole together define the confocal volume element. The detector signal is fed into a digital signal correlator, which calculates the autocorrelation function of the detected intensity fluctuations.