Figure 1.
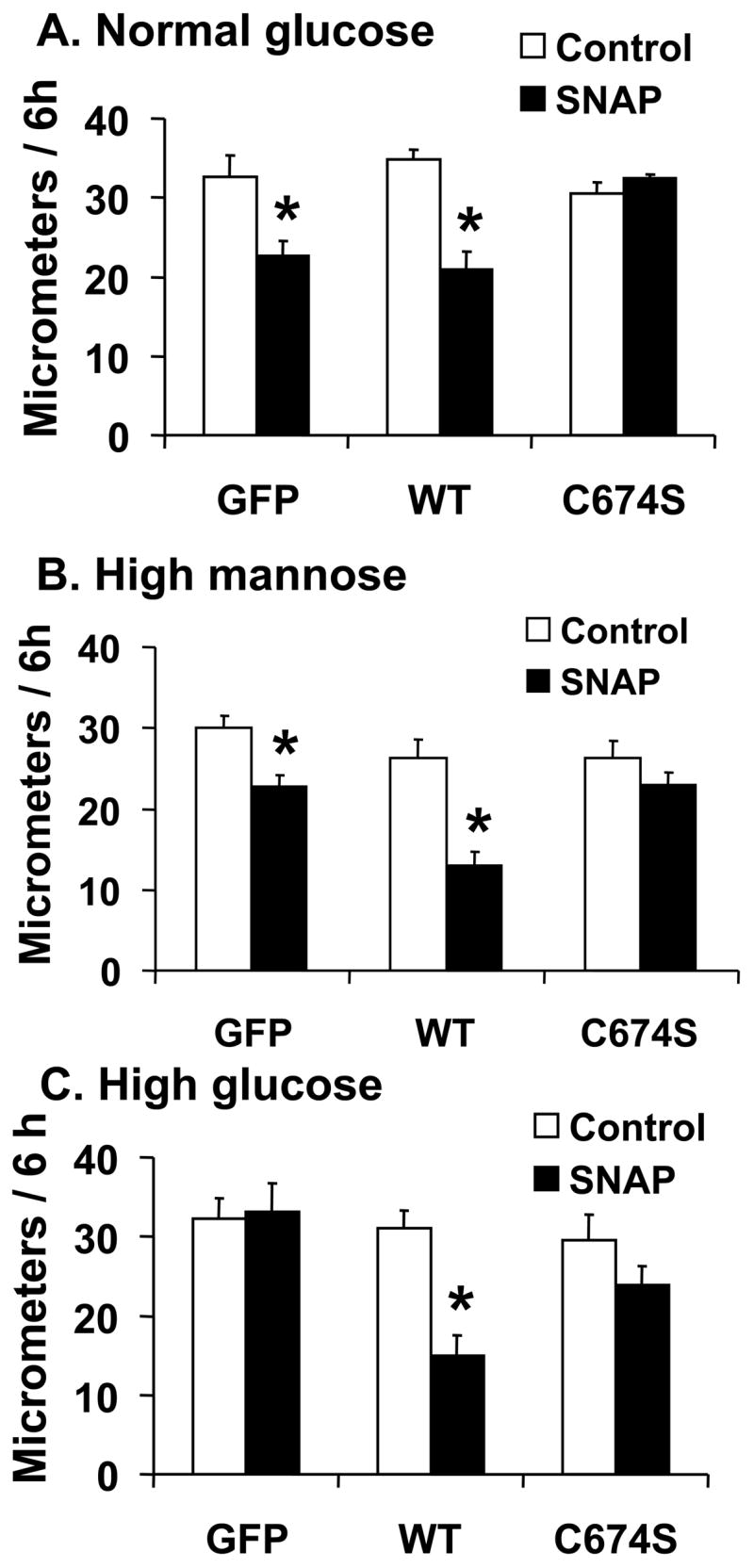
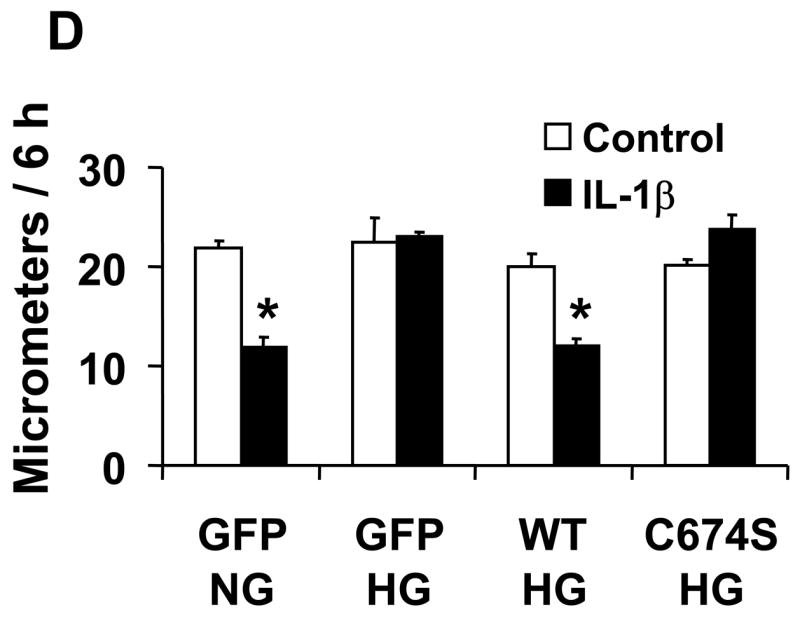
The effect of NO on the migration of rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC). A and B: NO donor SNAP significantly inhibited the migration of cells infected with either Ad-GFP or Ad-SERCA WT, but had no effect in cells infected with Ad-SERCA C674S in normal glucose (5.5 mmol/L) or high mannose (19.5 mmol/L plus glucose 5.5 mmol/L). C: In cells exposed to high glucose (25 mmol/L), SNAP did not inhibit migration. Overexpression of SERCA WT, but not SERCA C674S, preserved the ability of SNAP to inhibit migration. The results (A, B and C) are n=6 (mean ± SEM). *P<0.05, paired t-testbetween cells treated or not with SNAP. D: Cells were infected with Ad-WT or Ad-C674S SERCA for 2 d and then switched to medium containing NG or HG for an additional 3 days. Interleukin-1β (IL-1β, 5 ng/mL) was added 24 h before the migration assay to induce iNOS expression which releases NO. Ad-GFP served as a control. The results are n=5 (mean ± SEM). *P<0.05, paired t-test between cells treated or not with IL-1β.
