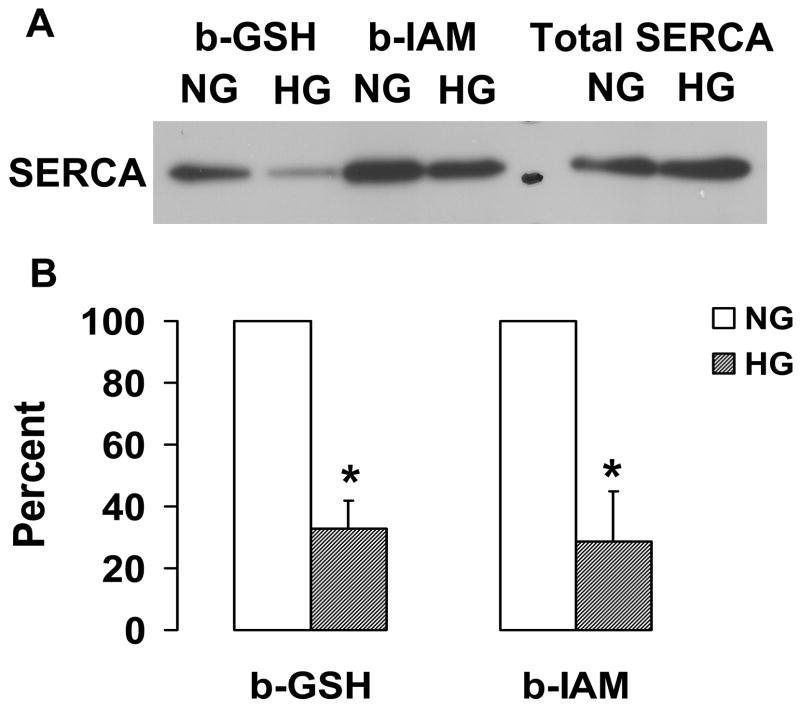
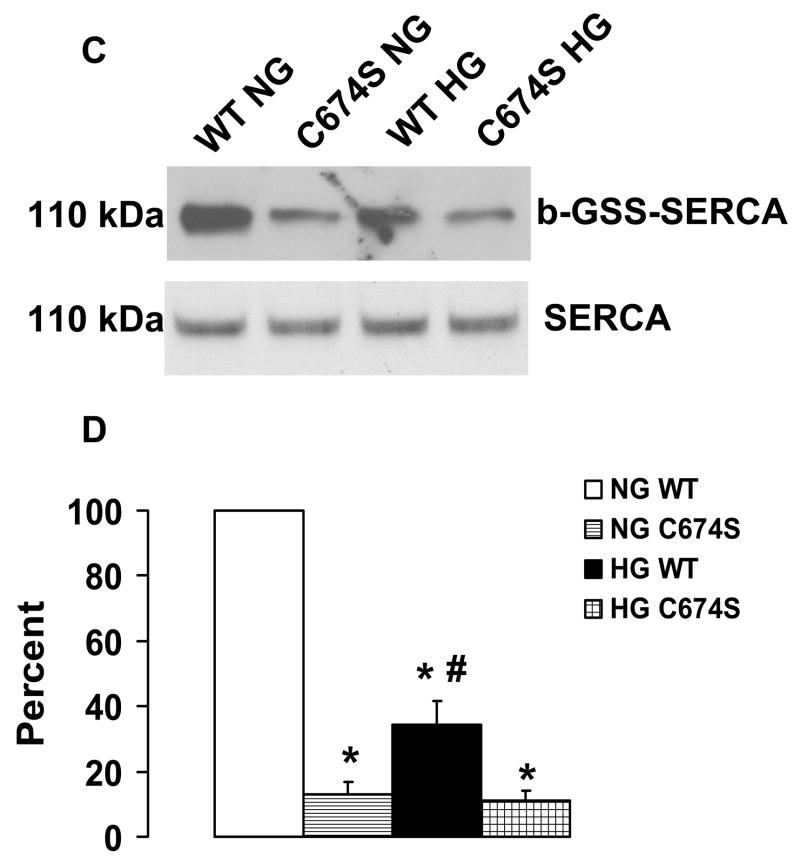
Figure 2.
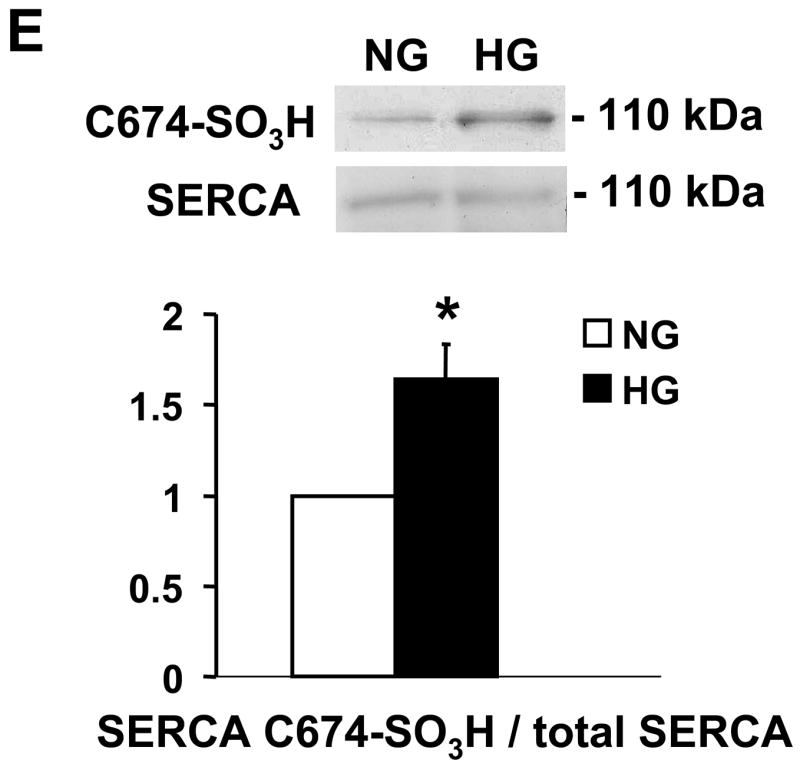
NO-induced biotinylated glutathione (b-GSH) and biotinylated iodoacetamide (b-IAM) labeling of SERCA and cysteine-674 sulfonic acid oxidation. A: b-GSH and b-IAM labeling of SERCA in uninfected VSMC exposed for 3 days to normal glucose (NG) or high glucose (HG). SERCA was detected with K30/A43 antibody. B: Bar graph shows summary of densitometry performed in three experiments indicating that both b-IAM labeling of SERCA and b-GSH binding to SERCA in uninfected VSMC exposed to HG were significantly less than that in NG. *P<0.05, paired t-test between cells treated with NG and HG. C. NO-induced S-glutathiolation of SERCA in VSMC infected with WT or C674S mutant SERCA exposed to NG or HG. SERCA was detected with IID8 910 antibody. D. Bar graph shows summary of 3 independent experiments indicating that NO-induced S-glutathiolation of SERCA was decreased in cells infected with SERCA WT exposed to HG compared to those exposed to NG (*P<0.05). Despite the fact that S-glutathiolation of SERCA was significantly decreased in cells infected with SERCA WT exposed to HG, the level remained significantly above that in cells infected with SERCA C674S mutant (# P<0.05). E: In membranes prepared from VSMC, a sequence-specific antibody against the SERCA cysteine-674 sulfonic acid shows increased detection in cells exposed to HG compared to cells exposed to NG. Total SERCA expression was not different. The bar graph in the lower panel summarizes 3 independent experiments showing that high glucose significantly increases the amount of the irreversible oxidation of SERCA expressed as the ratio of the densitometric values for detection with the SERCA C674-SO3H antibody with the total SERCA detected by the K30 antibody. *P<0.05, paired t-test.