Fig 1.
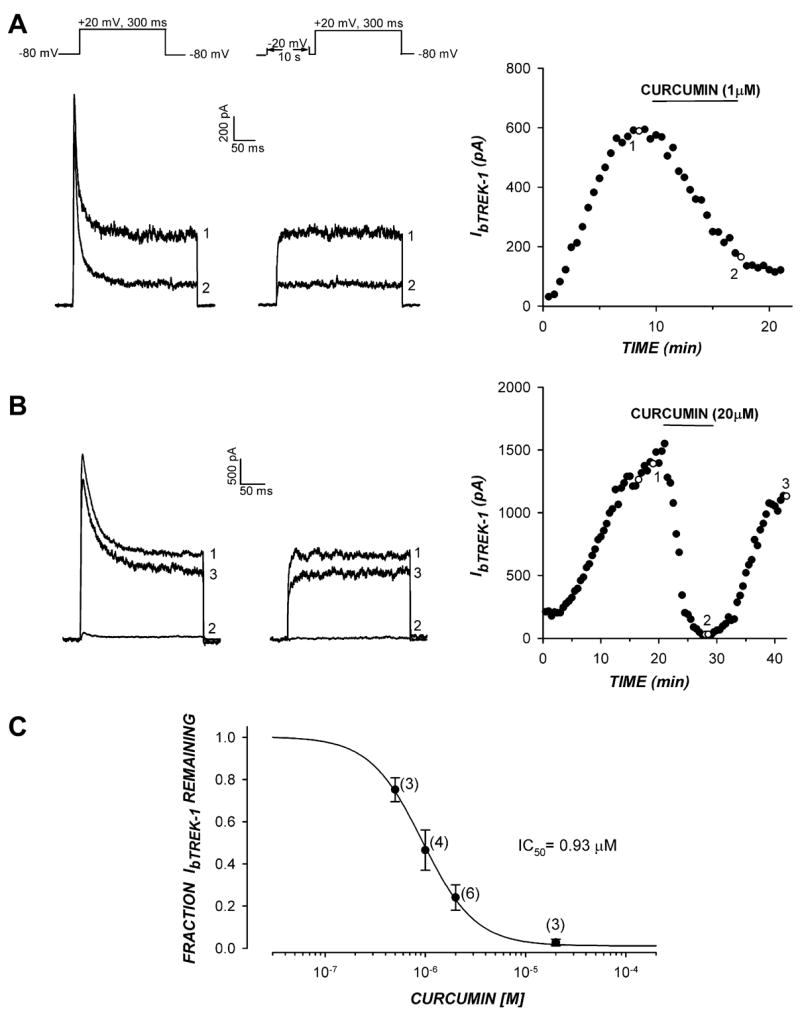
Curcumin inhibits bTREK-1 K+ channels. The inhibition of bTREK-1 K+ current by curcumin was measured in whole-cell patch clamp recordings from bovine adrenocortical cells. K+ currents were recorded at 30 s intervals in response to voltage steps to +20 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV with or without 10 s prepulses to −20 mV. After bTREK-1 reached a stable maximum amplitude, cells were superfused with saline containing curcumin at concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 20 μM. (A,B) K+ currents recorded with (right traces) or without (left traces) 10 s depolarizing prepulses to −20 mV. bTREK-1 amplitudes recorded with (open circles) or without (closed circles) prepulses are plotted against time. Numbers on traces correspond to those on plot. (C) Inhibition curve. Fraction of unblocked bTREK-1 current is plotted against curcumin concentration. Data were fit with an equation of the form: I/Imax = 1/[1 + (X/IC 50)B] were X is the curcumin concentration, B is the Hill coefficient, and IC50 is the concentration that reduces bTREK-1 by 50%. Values are means ± SEM of indicated number of determination.
