Fig 2.
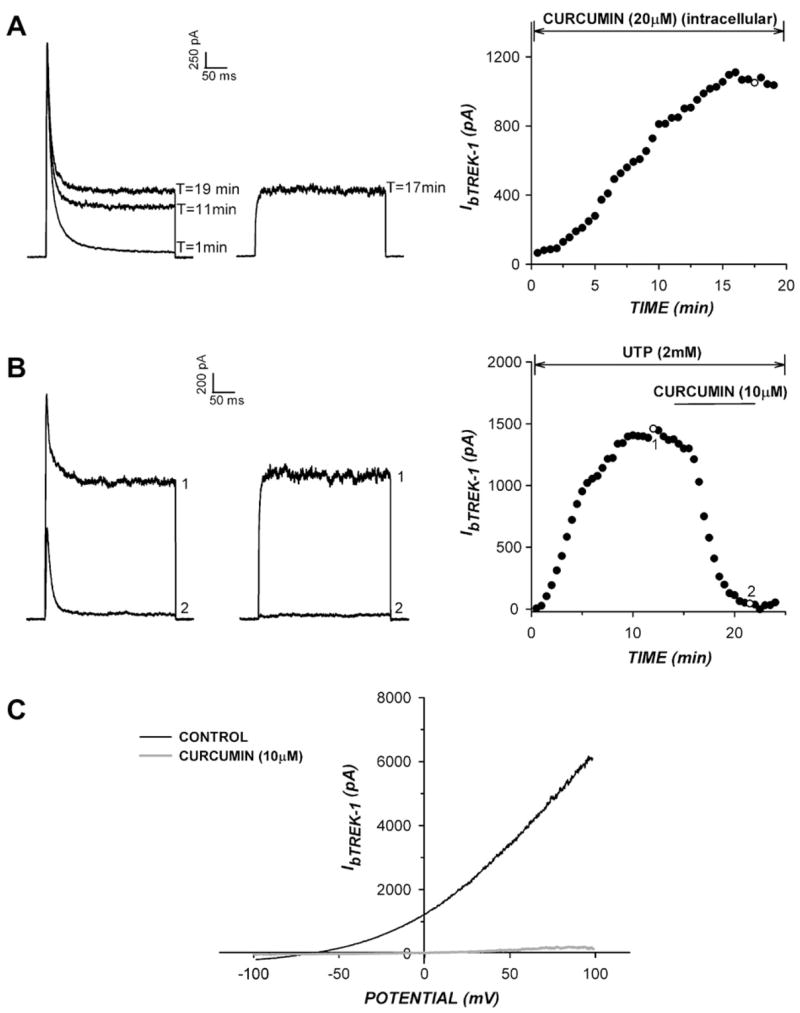
Characteristics of bTREK-1 inhibition by curcumin. (A,B) Curcumin blocks bTREK-1 directly at an external site. Whole-cell K+ currents were recorded in response to voltage steps to +20 mV, applied at 30 s intervals from a holding potential of −80 mV with or without 10 s depolarizing test pulses to −20 mV. (A) Effect of intracellular curcumin on bTREK-1 expression. Whole-cell K+ currents were recorded with (right traces) or without (left traces) depolarizing prepulses with a pipette containing curcumin (20 μM). Current amplitudes are plotted at right. B) Effect of UTP on TREK-1 inhibition by curcumin. K+ currents were recorded with (right traces) or without (left traces) depolarizing prepulses with a pipette containing 2 mM NaUTP in place of MgATP. Current amplitudes are plotted at right. Numbers on plot correspond to those on traces. C) bTREK-1 inhibition by curcumin is voltage-independent. bTREK-1 currents were activated in response to voltage ramps before and after superfusion of curcumin (10 μM). Voltage ramps were applied at 100 mV/s to potentials between +100 and −100 mV from a holding potential of 0 mV. Traces show currents before and after steady state block by curcumin.
