Figure 3.
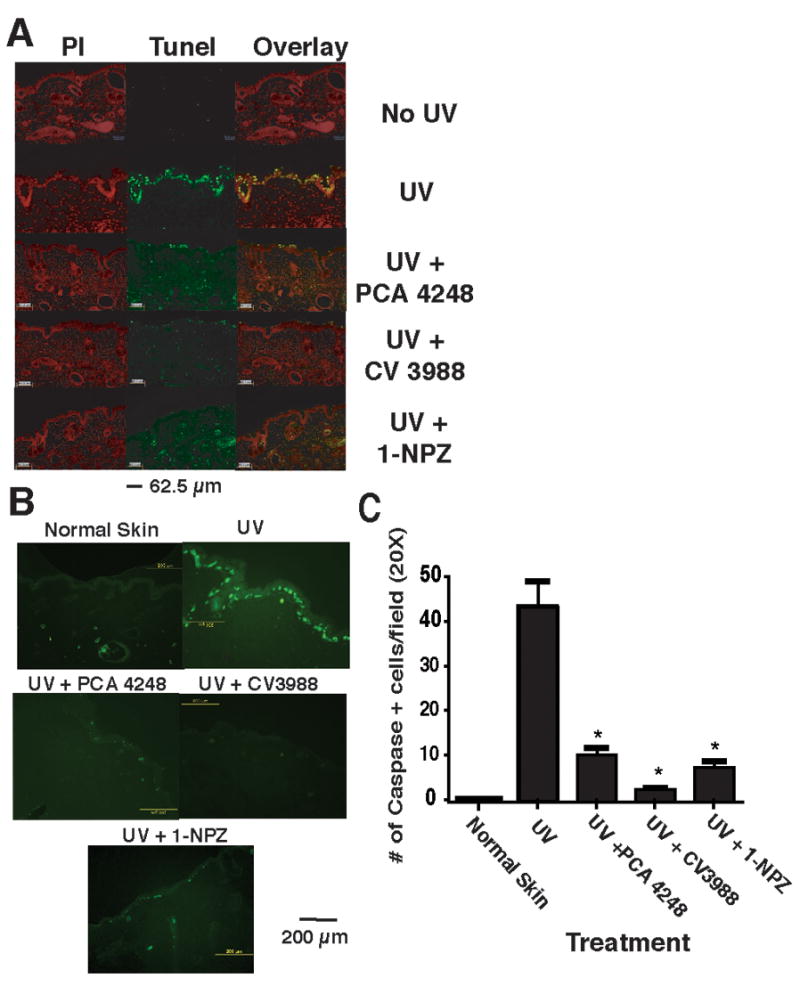
PAF and 5-HT2A receptor antagonists block UV-induced apoptosis. A: Apoptosis was determined by TUNEL staining. Skin sections taken after 24 h after exposing the mice to 1.5 kJ/m2 UVB radiation. Treatment groups include: Normal skin (No UV); UV only; mice injected with the PAF receptor antagonist PCA-4248 and exposed to UV; mice injected with the PAF receptor antagonist CV-3988 and exposed to UV; mice injected with the serotonin receptor antagonist 1-NPZ and exposed to UV. The left panel (red nuclear staining) shows propidium iodide staining. The middle panel shows TUNEL positive (green staining) cells. The overlay shows the merging of propidium iodide staining with TUNEL positive cells to confirm nuclear (yellow) staining. B: Immunofluorescence staining for active caspase-3. Skin sections were incubated with cleaved active caspase-3 antibody followed by a secondary antibody conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and visualized under a fluorescent microscope. Treatment groups include: Normal skin (No UV); UV only; mice injected with the PAF receptor antagonist PCA-4248 and exposed to UV; mice injected with the PAF receptor antagonist CV-3988 and exposed to UV; mice injected with the serotonin receptor antagonist 1-NPZ and exposed to UV. C: Enumeration of caspase-3 positive cells. * Indicates a significant reduction in caspase-3 positive cells in PAF and 5-HT2A receptor antagonists treated mice vs. UV control; p < 0.001.
