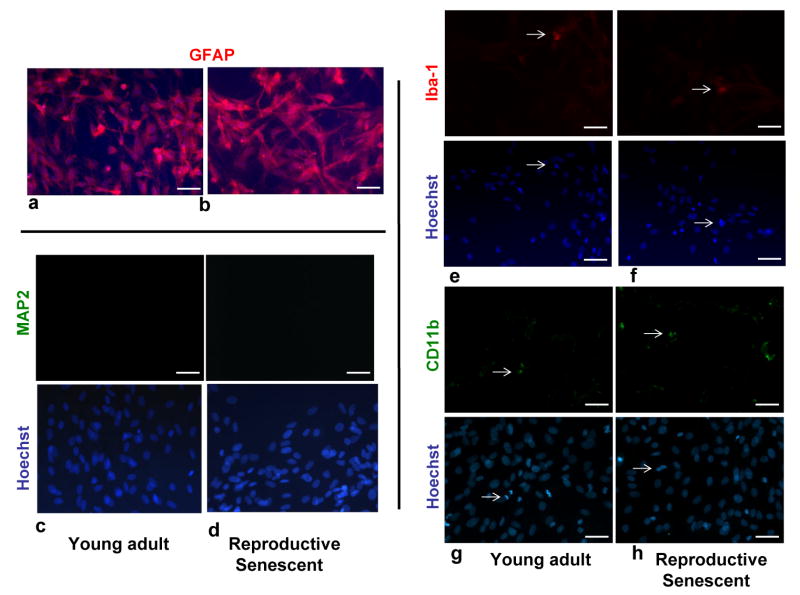
Figure 2.
Characterization of primary astrocyte cultures derived from the olfactory bulb of young adult and reproductive senescent female rats. Primary astrocytes cultures were immunoreactive for GFAP (red: a,b) and were counter-stained with the nuclear dye, Hoechst (blue). Primary astrocyte cultures derived from young adult (c) and reproductive senescent females (d) were not immunoreactive for the neuronal marker, microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP2). A small proportion (5-8%) of cells in these primary cultures derived from young adults (e,g) and reproductive senescent females (f,h) were immunopositive for the microglial markers, ionized-calcium binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba1) and the cell surface glycoprotein Mac-1 (CD11b). Iba-1 and CD11b immunopositive cells and their associated nuclei stained with Hoechst are indicated by white arrows. Immunohistochemistry with the nuclear dye Hoechst is shown in the bottom panel (c-h). Bar: 50 μm.