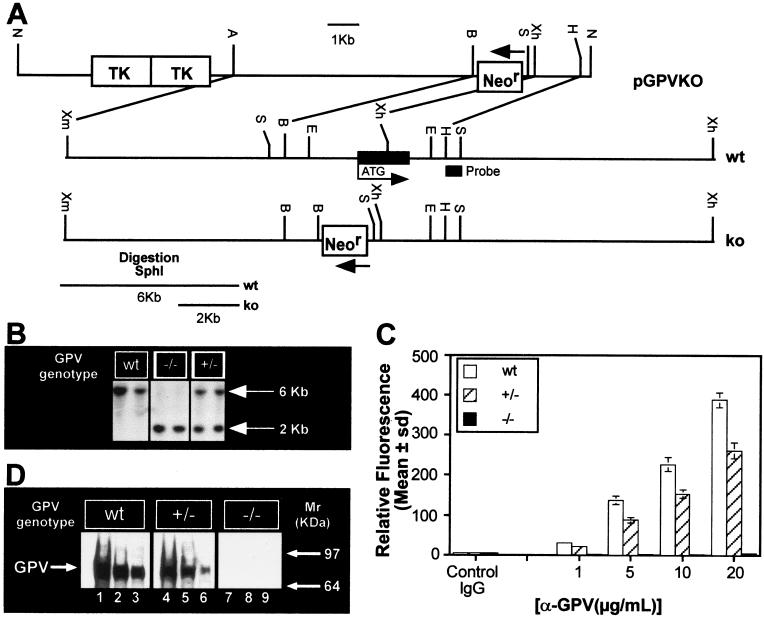
Figure 1.
(A) Genomic organization of the mouse GPV gene and generation of the targeting vector. The targeting vector pGPVKO contained a 5′ HR [8 kb; XmaI(blunt)–BamHI fragment of GP V] and a 3′HR (1.4 kb, XhoI–HindIII fragment of GP V) around the Neor cassette, as shown (B = BamHI, E = EcoRI, A = Acc651, H = HindIII, N = NotI, S = SphI, Xh = XhoI, Xm = XmaI). (B) Southern blot analysis of mouse-tail genomic DNA digested with SphI. The probe used is indicated in A. (C) FACS analysis of wt, +/− and −/− platelets. PRP from wt +/− and −/− mice was incubated with the indicated concentrations of Ab #810 and analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) Western analysis of GP V wt, +/− and −/− platelets. WP lysates were electrophoresed, transferred, and incubated with Ab #808 (5 μg/ml) followed by ECL. Lanes 1–3, wt, lanes 4–6, +/−, and lanes 7–9, −/−. Lanes 1, 4, 7: 2 × 107 platelets; lanes 2, 5, 8: 1 × 107 platelets; lanes 3, 6, 9: 5 × 106 platelets. Mouse GP V has a Mr ≈ 89,000 kDa.