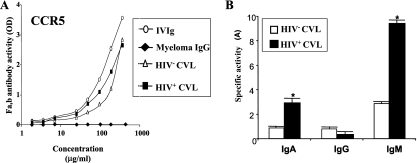
FIG. 2.
Autoantibody reactivities to CCR5. (A) CCR5 peptide CSSHFPYSQYQFWKNFQTLK, which corresponds to the second extracellular loop of CCR5 (II.E/C-CCR5), was coated on a 96-well plate; and serial dilution of i.v. Ig (open circles), IgG myeloma (bold diamonds), or pooled cervicovaginal secretions from HIV-seronegative women (HIV−; open triangles) or HIV-seropositive women (HIV+; bold square) were further added, as described in Materials and Methods. The concentration of CCR5-reacting antibodies was evaluated by the addition of biotin-conjugated mouse Ig against anti-human Fab, followed by the addition of streptavidin-peroxidase, and the results were revealed by substrate addition. The total Ig content (IgA, IgG, and IgM) of the preparations is shown on the abscissa. The results are expressed as the means of the values obtained from three independent experiments ± SDs. (B). Specific activities, in arbitrary units of IgA, IgG, and IgM NAbs, to CCR5 in pools of cervicovaginal secretions from HIV-seronegative healthy women (open squares) or HIV-seropositive women (bold squares) by isotype. The specific activities of antibodies of the IgA, IgG, or IgM isotype to the CCR5 peptide in CVL fluid samples were evaluated at the first dilution that gave an OD between 0.5 and 1.5 and per μg of total IgA, IgG, and IgM antibodies in CVL fluid samples, respectively, according to the formula A = (OD × d)/[Ig] (in μg/ml), as described previously (3, 40). The results are expressed as the means of the values obtained from three independent experiments ± SDs. *, P ≤ 0.05 by the paired Student t test between specific activities of CVL fluid samples from HIV-seronegative and HIV-seropositive women.