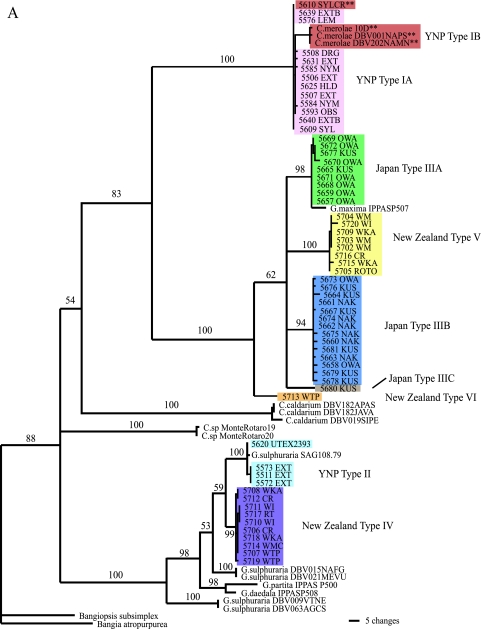
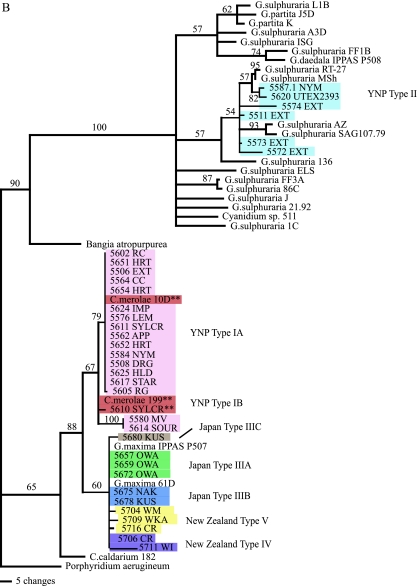
FIG. 2.
Maximum parsimony phylogenetic analysis of the cyanidial cultures described in this study. (A) Tree based on rbcL gene sequences using PAUP. The double asterisks represent those cultures with morphologies similar to that of C. merolae. Colors distinguish the various types. The reference strains (e.g., Cyanidium sp. Monte Rotaro 19 and Monte Rotaro 20 and most of the G. sulphuraria clusters [DVB 015, 021, 009, and 063]) may be found in reference 6. (B) Tree based on 18S rDNA gene sequences using PAUP. For both trees, branch lengths are proportional to the number of changes on a given branch, and bootstraps are given for each node above 50%. The double asterisks represent those cultures with morphologies similar to that of C. merolae. Colors of the various cultures correspond to the types indicated in panel A.