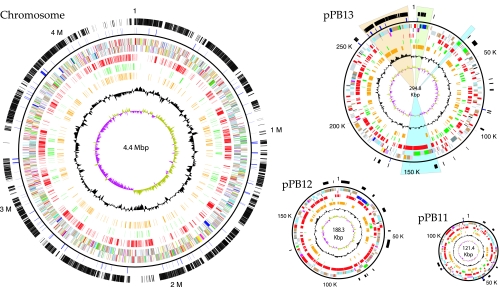
FIG. 1.
Genome of Nitrobacter hamburgensis X14 (ATCC 25391). The outer circle depicts the locations of genes conserved in all three sequenced Nitrobacter genomes. Genes that are conserved in Nitrobacter but not R. palustris or B. japonicum (the subcore) are indicated in the second circle. The third and fourth circles depict predicted protein-encoding and structural RNA genes in N. hamburgensis on the plus and minus strands, respectively (green, energy metabolism; red, DNA replication; magenta, transcription; yellow, translation; orange, amino acid metabolism; dark blue, carbohydrate metabolism; pale red, nucleotide metabolism; black, coenzyme metabolism; cyan, lipid metabolism; light blue, cellular processes; brown, general function; gray, hypothetical and conserved hypothetical genes; pale green, structural RNAs). Genes “unique” to N. hamburgensis (not present in N. winogradskyi or NB311A) are depicted in circle five (red). The sixth and seventh circles indicate the locations of all annotated pseudogenes (green) and paralogs (orange), respectively. The eighth circle indicates GC bias, and the ninth circle indicates GC skew. The highlighted region of pPB13 depicts the locations of key gene clusters: autotrophic island (peach), RuBisCO and pentose phosphate pathway genes (green), and the cytochrome oxidases (aa3 and bd-ubiquinol types) (blue).