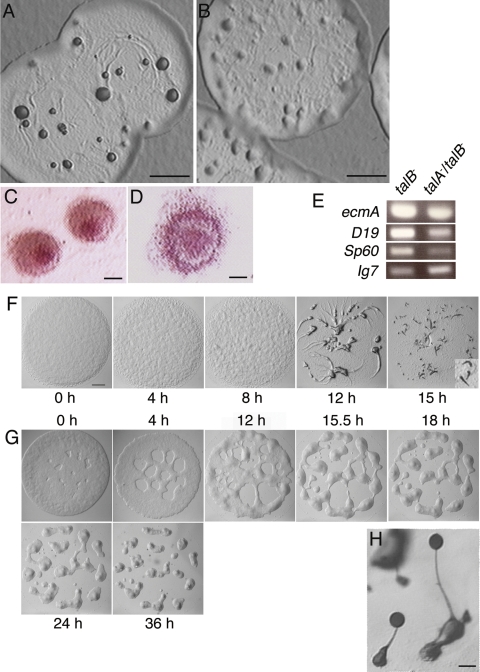
FIG. 6.
Development in the talA− talB− double mutant is arrested at an earlier stage than in the talB− single mutant. (A and B) Top views of the plaques on bacterial lawns of talB− (A) and talA− talB− (B) strains. Cells inside the edges of the plaques started morphogenesis due to starvation. (C and D) The mounds of talB− (C) and talA− talB− (D) mutants stained with neutral red. (E) RT-PCR analysis of the marker genes in the development of talB− and talA− talB− mutants. The expression levels of a prestalk-specific gene, ecmA, and two prespore-specific genes, SP60 and D19, were analyzed at the mound stage in talB− and talA− talB− mutants by RT-PCR using primer sets to amplify each gene fragment. Ig7 is a constitutively expressed gene used as the control. (F and G) The processes of mound formation in wild-type (F) and talA− talB− (G) strains. Slugs formed at 15 h in wild-type cells are magnified in the bottom right corner of panel F. (H) Fruiting bodies formed by talA− talB− cells expressing FLAG-tagged talin B. The scale bars represent 1 mm (A, B, and F), 100 μm (C and D), and 20 μm (H).