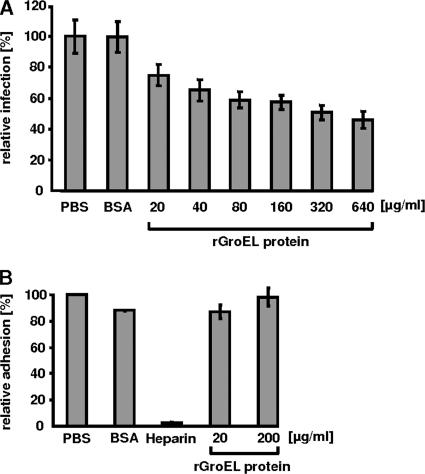
FIG. 7.
Soluble chlamydial rGroEL1 protein does not interfere with EB attachment to human cells but reduces subsequent infection by C. pneumoniae. (A) HEp-2 cells were incubated with increasing amounts (20 μg/ml to 640 μg/ml) of rGroEL1 for 2 h prior to infection with purified C. pneumoniae EBs. At 60 h postinfection, cells were fixed and analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy as described in Materials and Methods. HEp-2 cells pretreated with PBS or 200 μg/ml BSA prior to infection with C. pneumoniae served as controls. The number of chlamydial inclusions was determined, and the value found for the PBS control was set to 100% (n = 20 microscopic fields; number of experiments = 4). (B) Binding of purified, viable, CFSE-stained C. pneumoniae EBs to HEp-2 cells was detected by flow cytometric analysis. In control experiments, the attachment of C. pneumoniae EBs to HEp-2 cells incubated with PBS, 200 μg/ml BSA, or 500 μg/ml heparin was monitored and compared with binding rates in samples to which 20 μg/ml or 200 μg/ml rGroEL1 protein had been added (number of experiments = 4). Error bars indicate standard deviations.