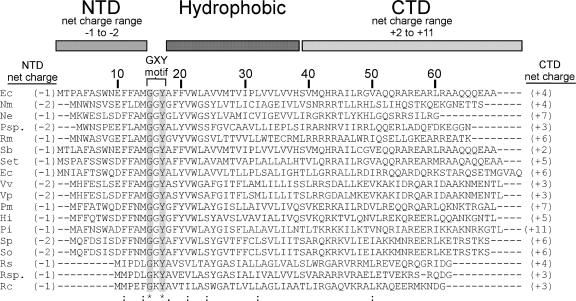
FIG. 1.
Alignment of the E. coli CcmD protein with representative bacterial CcmD sequences. The amino acid sequences of CcmD proteins of E. coli K-12 strain MG1655 (accession no. POABM5) (Ec), Nitrospira multiformis ATCC 2516 (YP_411906) (Nm), Nitrosomonas eutropha C71 (YP_747848) (Ne), Polynucleobacter sp. strain QLW-PIDMWA-1 (Psp.), Ralstonia metallidurans CH34 (YP_584534) (Rm), Shigella boydii Sb227 (YP_408515) (Sb), Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhi CT1 (NP_456796) (Set), Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica SCRI1043 (YP_049982) (Ec), Vibrio vulnificus YJ016 (NP_935245) (Vv), Vibrio parahaemolyticus RIMD 2210633 (NP_798599) (Vp), Pasteurella multocida subsp. multocida PM70 (NP_244945) (Pm), Haemophilus influenzae Rd KW20 (NP_439249) (Hi), Psychromonas ingrahamii 37 (ZP_01349302) (Pi), Shewanella putrefaciens CN-32 (ZP_00815699) (Sp), Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 (NP_715900) (So), Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1 (YP_351852) (Rs), Roseovarius sp. strain 214 (ZP_01034520) (Rsp.), and R. capsulatus SB1003 (P29963) (Rc) were aligned with ClustalW (25). Amino acid similarities are indicated as follows: asterisk and gray shading, identical residues in all sequences; colons, conserved substitution; and period, semiconserved substitution. The predicted domain structure of side chains, the net charges ([R + K] − [D + E]) of the NTD and CTD, and the location of the GXY motif are also indicated.