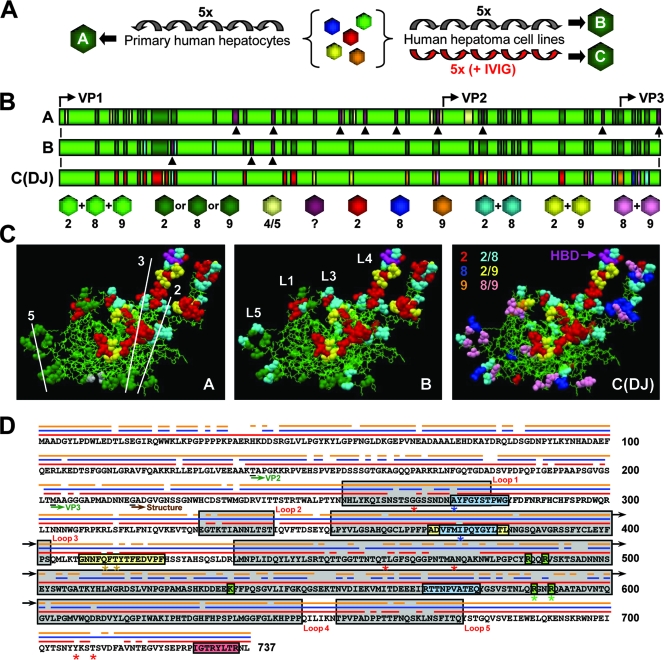
FIG. 2.
Molecular evolution of AAV vectors via DNA family shuffling. (A) The AAV capsid library was serially amplified on primary or transformed human liver cells. Purified human Igs (IVIG) were added to increase the selection pressure and to force vector evolution. Each scheme yielded a distinct pool of viral capsids (pools A to C). The alignment of ≥96 clones per pool with the sequences of the eight parental viruses confirmed the enrichment with specific sequences in association with increasing selection pressure. 5x, five times. (B) First 217 amino acids of the VP1 capsid protein for each pool. Colors represent the relationships to the parental strains (serotypes 2, 4, 5, 8, and 9), as also shown and detailed in Fig. S3 in the supplemental material. Arrowheads represent point mutations. Start codons for all three capsid proteins are shown. Pool C contained a single clone, designated AAV-DJ. (C) Putative atomic structure for each pool (the previously reported AAV-2 structure [Protein Data Bank file 1LP3 {http://www.rcsb.org}] was used as the basis for modeling; this structure lacks the residues represented in panel B). Thin green lines indicate sequence homology among the AAV-2, AAV-8, and AAV-9 parents. Residues shown as colored balls were derived from a subset of parental strains (see panel B for color codes; note that beige symbolizes AAV-5 in pool A here). AAV capsid symmetry axes (pool A) and four of the five loops (pool B) are shown. The location of two arginines as part of the conserved HBD (37) at the tip of loop IV is shown for AAV-DJ (pool C). (D) Capsid protein sequence of AAV-DJ. The three parental viruses are shown as thin lines above the sequence (AAV-2, red; AAV-8, blue; AAV-9, orange). Locations of the capsid loops, VP start codons, and the first residue of the atomic structure are indicated. A20 and B1 epitopes are boxed in blue and red, respectively (two mutations in the A20 epitope are shown by blue asterisks). Two recently identified immunogenic AAV-2 peptides (47) are boxed in yellow (AAV-DJ carries three point mutations, indicated by asterisks). Residues in green boxes form the conserved AAV-2 HBD (asterisks denote two arginines mutagenized in this study). Red asterisks denote residues previously discovered using other methods and believed to determine AAV-2 immunogenicity (see the text).