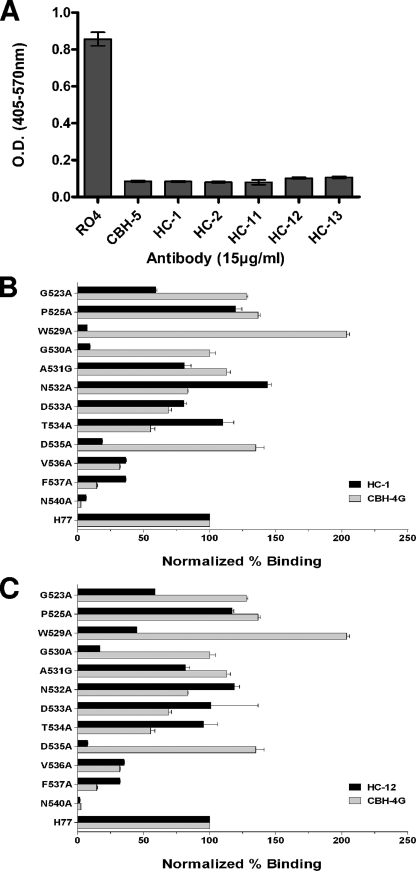
FIG. 4.
Inhibition of E2 binding to CD81 by HC HMAbs and location of critical residues involved in their epitopes. (A) Genotype 1a H77c E1E2 expressed in 293T cells containing 1 μg/ml E2 was incubated with each test HMAb at 15 μg/ml, and the antibody-antigen complex was then added onto CD81-precoated wells. Detection of E2 bound to CD81 was measured with biotinylated CBH-4D (12). CBH-5 was used as a positive control and RO4 as a negative control. The experiments were performed twice in triplicate. Error bars indicate one standard deviation from the mean. (B and C) Epitope mapping of the two representative HC HMAbs, HC-1 and HC-12, by alanine replacement. Mutated E2 proteins were expressed in 293T cells and analyzed by ELISA as described previously (11). The mutated amino acids are shown on the y axis. The numbers at the beginning of the peptides correspond to the position in the polyprotein of reference strain H (GenBank accession no. AF009606). HC HMAb binding to each mutant is expressed as the percentage of the binding value normalized by the binding of CBH-17 (6) and divided by HC HMAb binding to the wild type on the x axis.