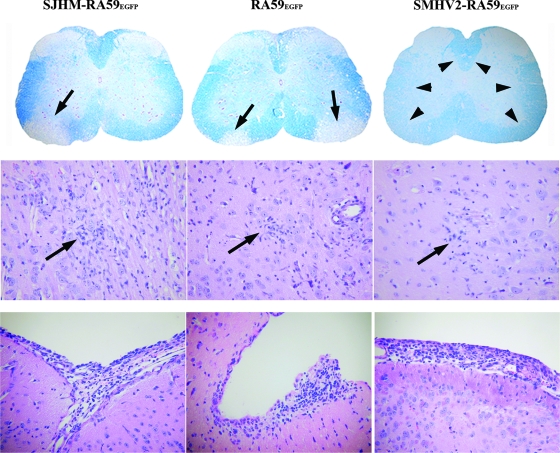
FIG. 2.
CNS pathology of EGFP-expressing MHVs. The upper panel shows the observed demyelination. Luxol fast blue stained spinal cord sections of mice infected with SJHM-RA59EGFP, RA59EGFP, or SMHV2-RA59EGFP, at day 30 postinfection. Thin arrows indicate a region of demyelination, and arrowheads indicate normal myelinated area of white matter. Original magnification, ×20. The middle panel shows the observed encephalitis. The microglial nodules shown are from H&E-stained basal forebrain sections of mice infected with EGFP-tagged MHVs at day 7 postinfection. Arrows indicate the microglial nodules (microglia with elongated nuclei) and lymphocytes in the vicinity of neurons in mice infected with SJHM-RA59EGFP, RA59EGFP, and SMHV2-RA59EGFP. Original magnification, ×200. The lower panel shows the observed meningitis. H&E-stained sections from the basal forebrain of mice infected with EGFP-tagged MHVs at day 7 postinfection; shown are SJHM-RA59EGFP, RA59EGFP, and SMHV2-RA59EGFP. In all cases, there is a brisk leptomeningeal lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate. Original magnification, ×200.