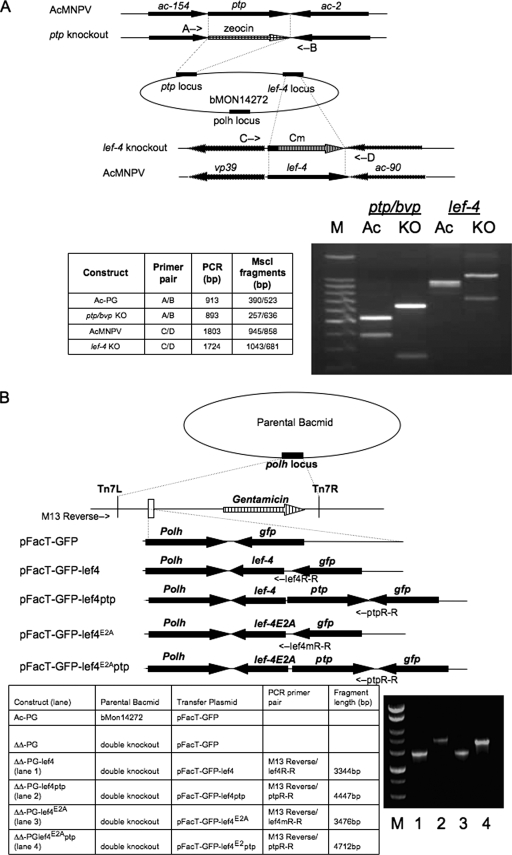
FIG. 1.
Construction of double-knockout and rescue bacmids. (A) Strategy for deletion of lef-4 and ptp/bvp genes. Schematic diagram showing location of genes and insertion of antibiotic resistance markers. Positions of primer pairs used to confirm disruption of lef-4 or ptp/bvp are shown by arrows. The table at the lower left summarizes predicted results for PCR-RFLP using appropriate primer pairs for each locus. Actual results are shown on the lower right. (B) Schematic diagrams of vAc-PG and rescue bacmids vAcΔΔRTPase-PGLEF-4, vAcΔΔRTPase-PGLEF-4/PTP, vAcΔΔRTPase-PGLEF-4E2A, and vAcΔΔRTPase-PGLEF-4E2A/PTP, showing the genes inserted into the polyhedrin (polh) locus by Tn7-mediated transposition. PCR analysis (on the bottom right) using the M13-reverse and specific gene primers, whose location is shown on the schematic diagram, to confirm transposition of the rescue constructs. The table shows templates, primers and expected PCR-RFLP sizes. KO, knockout; Ac, AcMNPV; M, 100-bp DNA size markers.