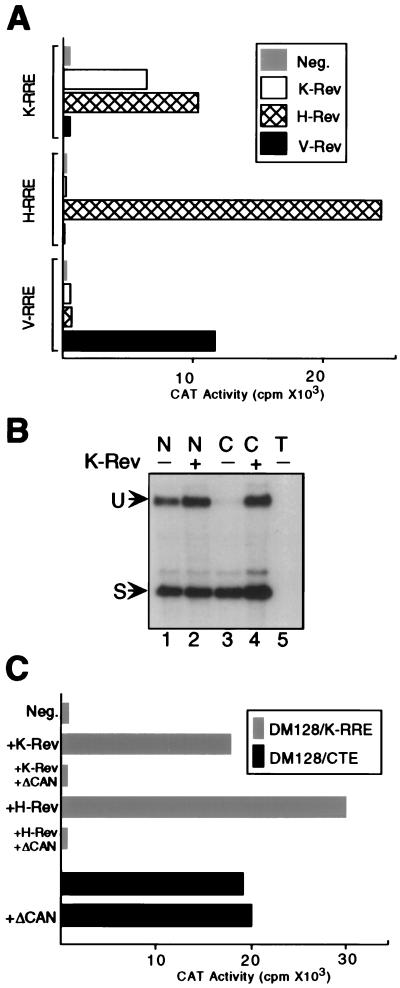
Figure 2.
K-Rev activates the cytoplasmic expression of an unspliced mRNA bearing the K-RRE. (A) Cells (293T) were cotransfected with a pDM128-based indicator construct bearing the K-RRE, H-RRE, or V-RRE, together with a pBC12/CMV-based expression vector encoding K-Rev, H-Rev, or V-Rev or with pBC12/CMV as a negative (Neg) control. pBC12/CMV/β-GAL was cotransfected as an internal control. At ≈48 h after transfection, cells were harvested, and induced CAT and β-GAL activities were determined. The presented data were corrected for minor variations in β-GAL activity and are representative of four independent experiments. (B) Cells (293T) were transfected with pDM128/K-RRE together with either pBC12/CMV/K-Rev (+) or the parental pBC12/CMV plasmid (−). At ≈48 h after transfection, nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) RNA fractions were isolated and analyzed by RNase protection assay by using a previously described (9) 32P-labeled RNA probe that traverses the 3′ splice site. Lane 5 contains total (T) RNA from mock-transfected 293T cells. U, unspliced RNA; S, spliced RNA. (C) Cells (293T) were transfected with pDM128/K-RRE and pBC12/CMV (Neg), pBC12/CMV/K-Rev, or pBC12/CMV/H-Rev, as described for A, except that an additional 500 ng of either pBC12/CMV/ΔCAN or pBC12/CMV was cotransfected. The pDM128/CTE indicator plasmid contains the MPMV CTE. Induced CAT and β-GAL activities were determined as described for A. ΔCAN does not significantly affect expression of the β-GAL internal control (6). These data are representative of three independent experiments.