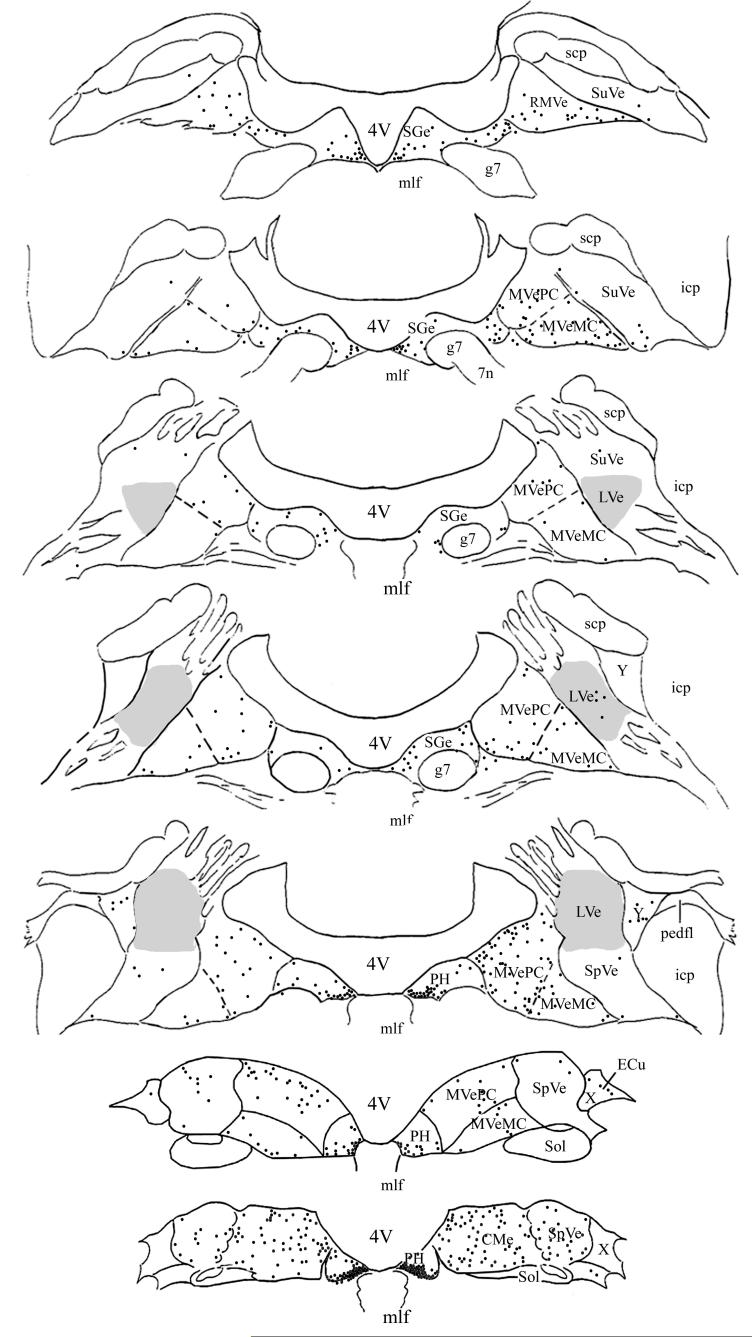
Figure 2.
Distribution of PRV-BA-immunopositive neurons in the vestibular nuclei and prepositus hypoglossi of one animal that survived 96 hrs following virus injections into the masseter muscle. The left side of the diagram depicts labeling that was ipsilateral to the injection site, whereas the right side shows contralateral labeling. The locations of transneuronally-labeled neurons were plotted on 7 representative sections, which were derived from Rubertone’s templates (Rubertone et al. 1995). Each black dot represents one infected cell. A shaded area demarks the lateral vestibular nucleus (LVe). Abbreviations: 4V, Fourth ventricle; 7n, root of facial nerve; CMVe, caudal portion of the medial vestibular nucleus; ECu, external cuneate nucleus; g7, genu of facial nerve; icp, inferior cerebellar peduncle; mlf, medial longitudinal fasciculus; MVeMC, magnocellular portion of the medial vestibular nucleus; MVePC, parvocellular portion of the medial vestibular nucleus; pedfl, floccular peduncle; PH, prepositus hypoglossi; RMVe, rostral portion of medial vestibular nucleus; scp, superior cerebellar peduncle; Sge, supragenual nucleus; Sol, nucleus of the solitary tract; SpVe, spinal vestibular nucleus, SuVe, superior vestibular nucleus; X, X-group; Y, Y-group.