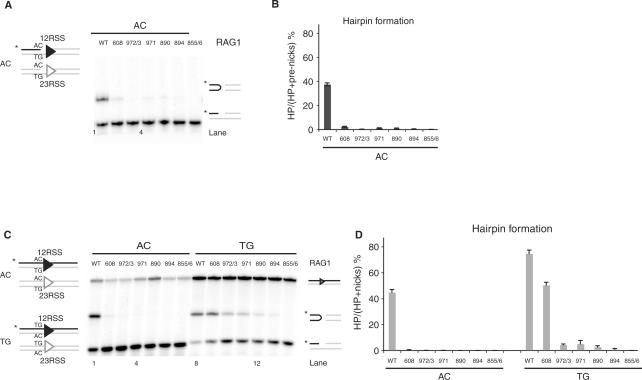
Figure 2.
Rag1 mutants exhibit defective hairpin formation. (A) In vitro cleavage assay using 12- and 23-RSS oligonucleotide substrates that mimic a nick on an AC flank, as depicted in schematic representation on the left. (B) Quantitation of gel in A, showing the percentage of pre-nicks converted to hairpins, was performed using ImageQuant software. Error bars represent SEM of three experiments. (C) In vitro cleavage assay using oligonucleotide substrates with either an AC or TG coding flank on both 12- and 23-RSS, as depicted on the left. Only the strands drawn as black lines were 5′-radiolabeled (*), and thus detectable after denaturing gel electrophoresis. The reaction was performed for 30 min, in the presence of paired 12- and 23-RSS oligonucleotides, purified Rag1 (wild-type or mutants) and Rag2 proteins, HMG and Mg2+. Reaction products were separated on a 12% sequencing gel and visualized by autoradiography. Reaction products are shown on the right (from top to bottom): uncleaved substrates, hairpin and nicks. (D) Quantitation of gel in C, showing the percentage of nicks converted to hairpins, was performed using ImageQuant software. Error bars represent SEM of three experiments.