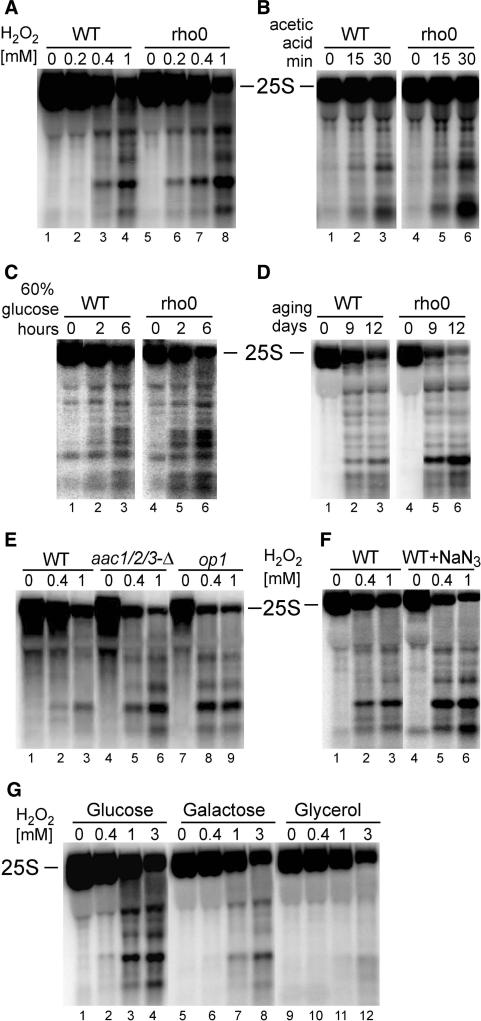
Figure 7.
Degradation of the 25S rRNA in apoptotic condition is related to mitochondrial respiration activity. Northern analysis, using probe 007 starting at position +40 of the 25S, of RNA from mutants or conditions where mitochondrial respiration is inhibited. (A–D) W303 wild-type or rho0 strains (lacking mtDNA) in different apoptotic conditions: treatment with varying amounts of H2O2 (A, WT lanes 1–4, rho0 lanes 5–8); treatment with 175 mM acetic acid for times indicated (B, WT lanes 1–3, rho0 lanes 4–6); exposure to hyperosmotic stress (60% glucose) for times indicated (C, WT lanes 1–3, rho0 lanes 4–6); chronological ageing for indicated numbers of days (D, WT lanes 1–3, rho0 lanes 4–6). (E) Mitochondrial ATP/ADP carrier mutants, aaa1/2/3-Δ (lanes 4–6) and op1 (lanes 7–9) and the isogenic wild-type (lanes 1–3) treated with increasing concentrations of H2O2. (F) Wild-type W303 strain, untreated (lanes 1–3) and treated with the respiration inhibitor sodium azide (NaN3, lanes 4–6), exposed to indicated concentrations of H2O2. (G) H2O2 treatment of wild-type W303 cells grown on different carbon sources: glucose (lanes 1–4), galactose (lanes 5–8) and glycerol (lanes 9–12).