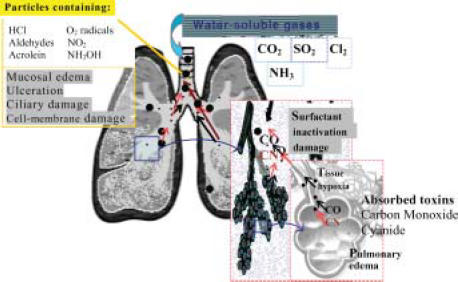
Figure 1.
Effect of the components of smoke on the lungs. Water-soluble gases are seen producing upper-airway irritation. The components on the carbon particles lead to more severe airways damage including cell membrane changes and, in some cases, alveolar damage. Carbon monoxide and cyanide are absorbed directly into the blood from the alveoli