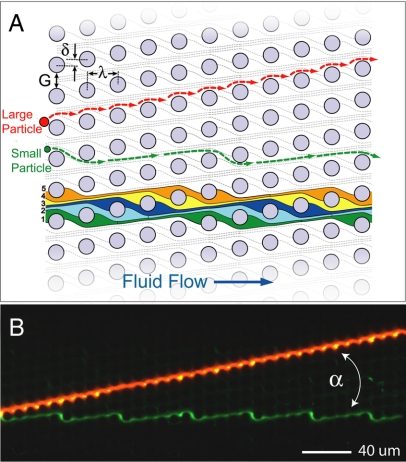
Fig. 1.
Size-based particle separation in an asymmetric array of posts. (A) Schematic of a deterministic lateral displacement (DLD) array showing definitions of the array parameters: The posts are periodically arranged with spacing λ; each downstream row is offset laterally from the previous row by the amount δ breaking the symmetry of the array. This array axis forms an angle α = tan−1(δ/λ) = tan−1(ε) with respect to the channel walls and therefore the direction of fluid flow. Because of the array asymmetry, fluid flow in the gaps between the posts G is partitioned into 1/ε slots delineated with individual colors. Each of these slots repeats every 1/ε rows so the flow through the array is on average straight. Particles transiting the gap near a post can be displaced into an adjacent streamline (from slot 1 to slot 2) if the particles radius is larger than the slot width in the gap. Therefore, larger particles (red) are deterministically displaced at each post and migrate at an angle α to the flow. Smaller particles (green) simply follow the streamline paths and flow through the array. (B) Separation of 2.7-μm red fluorescent beads and 1.0-μm green fluorescent beads by using the array (α = 11.3°, G = 4 μm, λ = 11 μm).