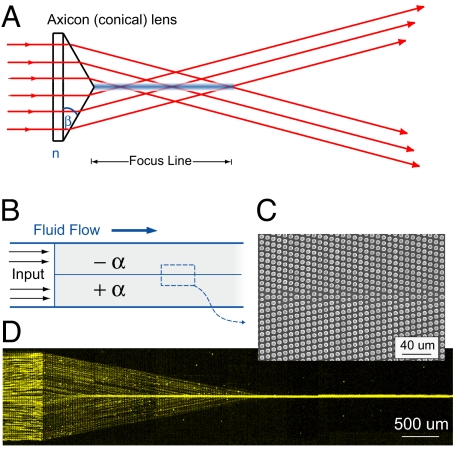
Fig. 5.
Optical and microfluidic focusing elements. (A) A conical lens or axicon focuses collimated incident light into a nominally nondiffracting line. (B) The microfluidic equivalent of a focusing lens is constructed by tiling a −α array and a +α array vertically. The focusing element +F directs incident particles to a line. (C) SEM image of the interface between the subelements. (D) Here, 2.7-μm diameter fluorescent particles enter the microfluidic device from a single inlet port and are rapidly focused within a few channel widths into a continuously flowing hydrodynamic jet.