Figure 3.
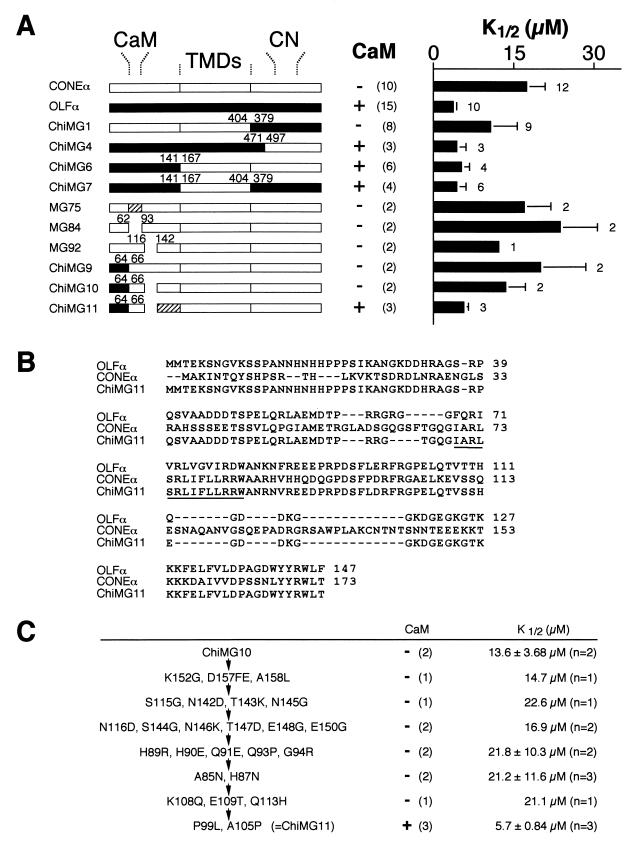
Experiments to identify additional elements besides the CaM-binding site that are necessary to produce a CaM effect on human CONEα. (A) (Left) Schematic diagrams indicating the structures of various chimeras and mutants from rat OLFα and human CONEα. The locations of the CaM-binding site, the cyclic nucleotide-binding site, and the boundaries of the transmembrane domains (TMDs) are indicated. Numbers indicate the last and first residues of the respective sequences at the junctions or deletions. MG84 has the CaM-binding site deleted. MG92 has a stretch of residues (A117–T141) on CONEα deleted to match up the sequence length on OLFα downstream of the CaM-binding site. Hatched region indicates a region in which the CONEα sequence is modified. For MG75, the mutations A71Q, S74V, F78G, and R82D have been carried out in the CaM-binding site of CONEα to make it more resemble that on OLFα. For ChiMG11, the serial mutations are detailed in C. Two other chimeras were made but did not produce any cGMP-activated current when expressed: one with a CONEα N terminus in an OLFα background and the other with OLFα TMDs in a CONEα background. (Center) Presence (+) or absence (−) of a CaM effect, assayed electrophysiologically as in Fig. 2 with a nonsaturating concentration of cGMP and 50 μM Ca2+ and 250 nM CaM; the number in parentheses indicate number of experiments, some of which were in common with those at right. (Right) cGMP K1/2 values (at −60 mV) for the respective constructs in the absence of CaM and Ca2+, estimated by using three or more concentrations of cGMP. Averaged data with SDs and numbers of experiments are indicated. (B) Sequence alignments of the N-terminal regions of rat OLFα, human CONEα, and ChiMG11 by using the clustalw algorithm. The CaM-binding region is underlined. (C) Serially cumulative mutations (as indicated by flow arrows) to generate ChiMG11 from ChiMG10. The residues mutated are numbered according to the wild-type CONEα sequence. The depictions of CaM effect and cGMP K1/2 values in control conditions have the same meanings as in A.