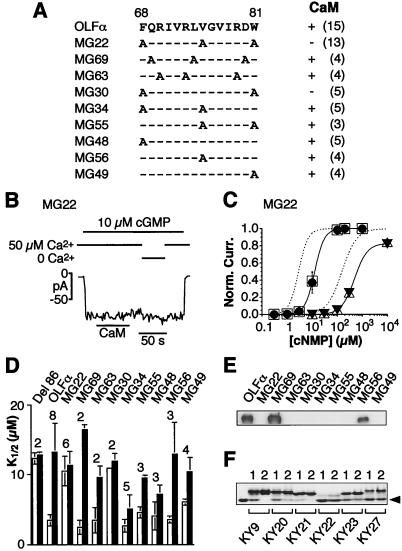
Figure 4.
Analysis of the CaM-binding site on rat OLFα. (A) Amino acid sequence of the binding site and the introduced mutations. For each mutant, alanine replaced the wild-type residue at the indicated positions. (Right) Presence or absence of a CaM effect, assayed as in B; the number in parentheses indicates number of experiments. More detailed data on K1/2 in the absence and presence of CaM, assayed as in C, are shown in D. (B–D) Electrophysiological analysis of homomeric channels formed by each of the mutant proteins, using patch-clamp recordings from excised, inside-out membrane patches of transfected HEK 293 cells. Voltage was at −60 mV throughout. (B) Loss of the CaM effect for mutant MG22. CaM was at 250 nM. (C) Dose–response relations between activated current and concentration of cyclic nucleotide for MG22 in the presence of 50 μM Ca2+ and with (filled symbols) or without (open symbols) 250 nM CaM. Circles and squares, cGMP; triangles, cAMP. Averaged data from three patches for cGMP and two for cAMP; vertical bars are SDs. Curve fits are according to the Hill equation. Dashed lines represent curve fits for averaged data (not shown) from wild-type OLFα, for cGMP and cAMP, respectively, in control conditions (50 μM Ca2+ but no CaM). For cGMP, K1/2 = 12.7 μM and n = 2.2 without CaM, and K1/2 = 12.1 μM and n = 2.4 with CaM. For cAMP, K1/2 = 491 μM and n = 1.7 without CaM, and K1/2 = 481 μM and n = 1.8 with CaM. (D) Measured cGMP K1/2 values for the various mutant channels in the absence (open bars) and presence (filled bars) of 250 nM CaM. Averaged data and SDs, with the number above each bar indicating the number of experiments; for MG30, the SD for the open bar is too small to be depicted. The same procedure as in C was used. Del 86 lacks the entire CaM-binding site (12). In the presence of CaM, some of the mutants have lower K1/2 values compared with, e.g., wild-type OLFα, presumably because of a weaker affinity of the binding site for CaM, so that 250 nM CaM was unable to occupy all of the sites. (E) Gel-overlay experiment with biotinylated CaM and GST–fusion proteins of the N terminus of OLFα having the various mutations in the binding site. After the CaM overlay, the blots were stripped and probed with an α-GST antibody, and the results indicated roughly the same amount of protein in each lane (data not shown). (F) Gel-shift experiment with CaM and peptides corresponding to some of the mutants shown in A, D, and E. Peptide KY9 corresponding to amino acids 62–87 on wild-type OLFα. KY20 (MG48), KY21 (MG49), KY22 (MG63), KY23 (MG30), and KY27 (MG22) correspond to the same OLFα sequence except for the indicated mutations. Two hundred-fifty picomoles of CaM and a peptide in peptide/CaM mole ratios of 1 or 2 (indicated above each lane), plus 2 mM Ca2+, was used in each case. The leftmost lane contains CaM but no peptide. The arrowhead indicates the position of free CaM. No shifts were observed without Ca2+ (data not shown). Note that KY22 and KY27 gave the least shift of the CaM band, suggesting least affinity for CaM.