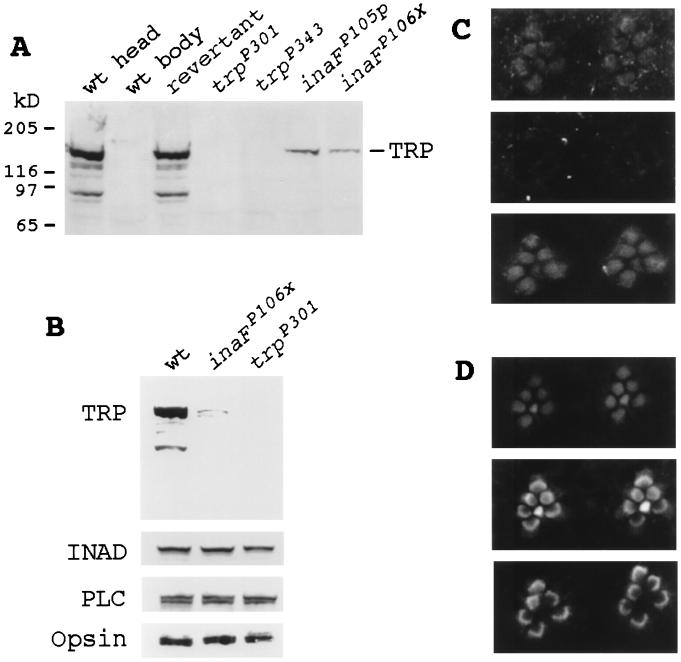
Figure 3.
Immunodetection of the TRP protein. (A) Western blot analyses of null and near-null inaF and trp mutants and wild-type and revertant controls. The seven lanes were loaded with total protein prepared from wild-type heads, wild-type bodies, revertant heads, trpP301 heads, trpP343 heads, inaFP105p heads, and inaFP106x heads (lanes 1 to 7, respectively). The blot was probed with a monoclonal anti-TRP Ab (23). (B) Western blot analysis with retinal protein controls. The three lanes were loaded with total protein prepared from wild-type heads, inaFP106x heads, and trpP301 heads, and the blot was probed with, from top to bottom, anti-TRP, anti-INAD, anti-PLCβ, and anti-opsin Abs, respectively. (C) Subcellular localization of the TRP protein by immunofluorescence confocal microscopy. (Top) Confocal micrograph of the rhabdomeres of the inaFP106x compound eye labeled with a TRP antiserum and visualized with an FITC-conjugated secondary Ab. TRP-specific staining is found only in rhabdomeres. (Middle) Confocal micrograph of trpP301 rhabdomeres, processed exactly the same as for inaFP106x (see Methods). There is no TRP-specific staining. (Bottom) Confocal micrograph of exactly the same field and focal plane of trpP301 rhabdomeres as Middle, but showing staining of filamentous actin in rhabdomeres. The preparation was double-labeled with a TRP antiserum and phalloidin (see Methods). (D) Subcellular localization of control retinal proteins in inaF by confocal microscopy. Confocal micrographs of inaFP106x retinas labeled with anti-INAD (Top), anti-PLCβ (Middle), and anti-opsin (Bottom) Abs and visualized with an FITC-conjugated secondary Ab.