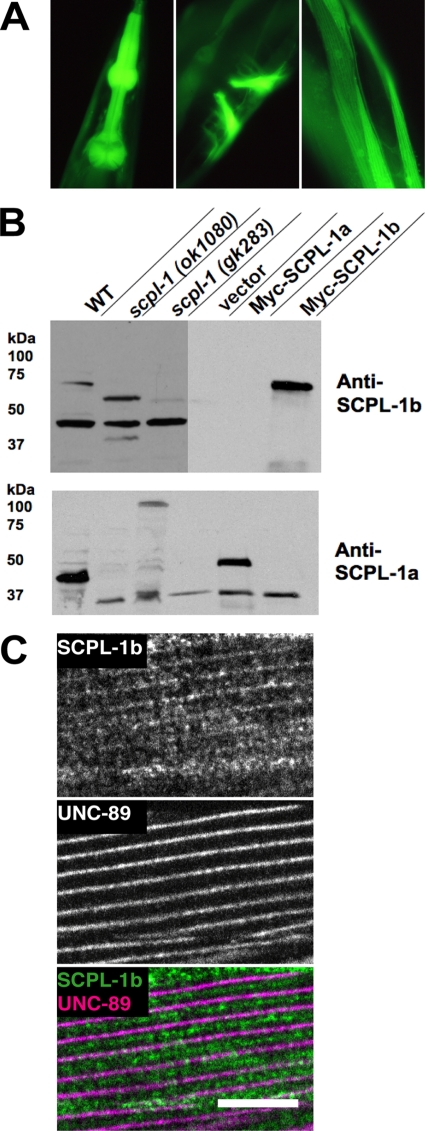
Figure 4.
Expression pattern of the SCPL-1b promoter and characterization of antibodies to SCPL-1. (A) SCPL-1b is expressed in the same muscle cells as UNC-89. The exon/intron structure of the SCPL-1b gene is shown, as predicted on WormBase. 7.5 kb of DNA sequence upstream of the initiator methionine together with codons for a few amino acids of the first exon of SCPL-1b were fused in-frame with GFP, and used to create transgenic animals, and the sites of GFP expression were recorded. This promoter is expressed in pharyngeal (left), vulval (center), and body wall muscle (right). (B) Anti-SCPL-1b and anti-SCPL-1a antibodies specifically recognize SCPL-1b and SCPL-1a, respectively. Above is shown immunogens used to generate rabbit antibodies that were later affinity purified using the same regions. Below are Western blots reacted with the designated antibodies. In each case, the left-most three lanes are worm extracts, and the right-most lanes are yeast extracts. WT, wild type; scpl-1(ok1080) and scpl-1(gk283) are intragenic deletions of the scpl-1 gene. Vector, Myc-SCPL-1a, and Myc-SCPL-1b are yeast harboring either the empty vector or myc-tagged SCPL-1 isoforms. (C) Anti-SCPL-1 localize to M-lines and I-bands in body wall muscle. Anti-SCPL-1b and anti-UNC-89 were coincubated with wild-type worms, and the muscle was imaged by immunofluorescence microscopy. The images show a portion of one body wall muscle cell. Weak labeling of the M-line and a portion of the I-band is seen. UNC-89 is a marker of the M-line. Bar, 10 μm.