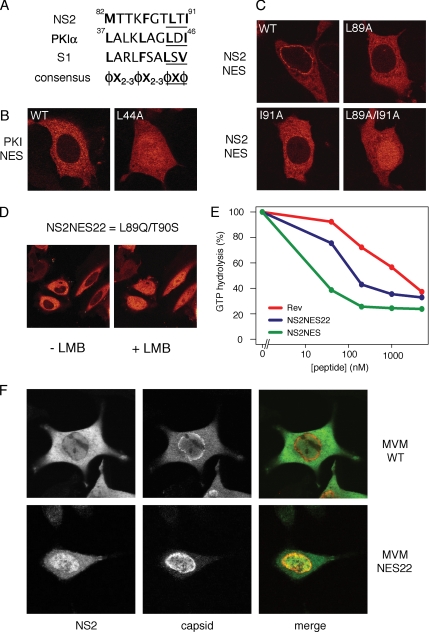
Figure 6.
The NS2 supraNES is functionally required for viral nuclear export and infectivity. (A) Comparison of NES sequences of NS2, PKIα, and S1. Hydrophobic residues are marked bold. The core regions of the NESs are underlined. φ: L, I, F, M, or V; X: any other residue. (B and C) MCF7 cells were transfected with GFP-tagged NESs for 24 h. (B) Export of the PKIα-NES is inhibited upon mutation of one hydrophobic residue. (C) A single mutation in the NS2 supraNES downgrades the supraNES to a regular NES. To inactivate the NES activity an additional hydrophobic residues needs to be mutated. (D) NES22 behaves like a regular NES. Cells were transfected with GFP-NES22 and imaged using live confocal microscopy. + LMB: cells were treated with LMB for 10 min. (E) NES22 retains CRM1 binding activity NES. Affinity of NES22 was tested in GAP assay as described in Figure 2A. Synthetic peptides were used. NES22 (blue), supraNES (green), and RevNES (red). (F) NES22 viruses fail to be exported and the NS2-NES22 protein is retained in the nucleoplasm. Mouse fibroblasts expressing the WT or NES22 genome for 42 h were stained with anti-NS2 and anti-capsid antibodies.