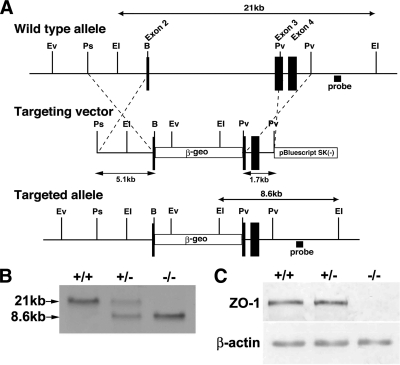
Figure 1.
Generation of ZO-1–deficient mice. (A) Restriction maps of the wild type allele, the targeting vector, and the targeted allele of the ZO-1 gene. The targeting vector contained the pgk-neo cassette in its middle portion to delete the two to three exons in the targeted allele. The position of the probe for Southern blotting is indicated as a bar (Probe). Ev, EcoRV; Ps, PstI; EI, EcoRI; B, BsrDI; and Pv, PvuII. (B) Genotypic analysis by Southern blotting of EcoRI-digested genomic DNA from wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/−), and homozygous (−/−) mice for the ZO-1 gene allele. Southern blotting with the probe indicated in A yields 21- and 8-kb bands from the wild-type and targeted allele, respectively. (C) Loss of ZO-1 protein in the embryonic extract of Tjp1−/− mice examined by immunoblotting. Anti-ZO-1 immunoblotting of the embryonic protein extracts of ZO-1–deficient mice. Embryonic protein extracts (10 μg) from Tjp1+/+ (+/+), Tjp1+/− (+/−), and Tjp1−/− (−/−) mice were immunoblotted with anti-ZO-1 mAb. In the wild-type and heterozygous embryonic extracts, the ZO-1 band is detected, whereas in the homozygous extract, this band is not detected.