Abstract
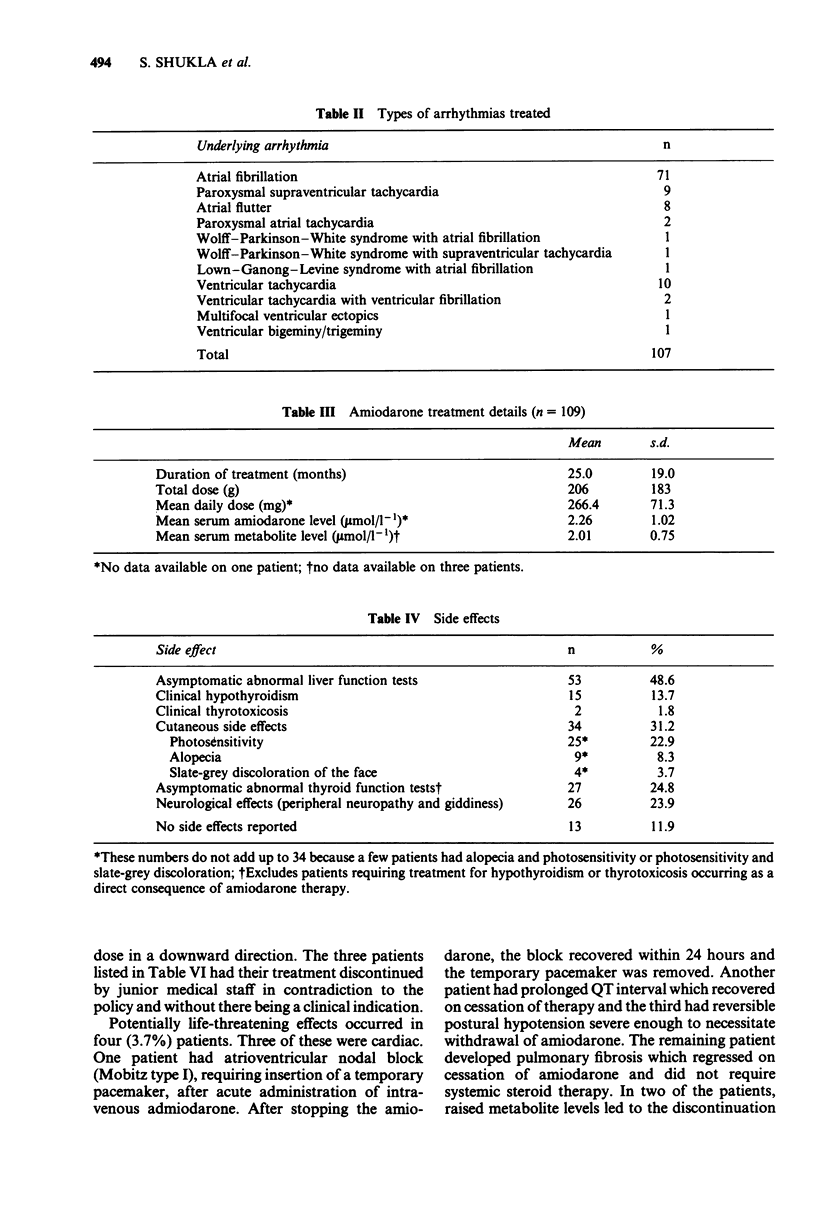
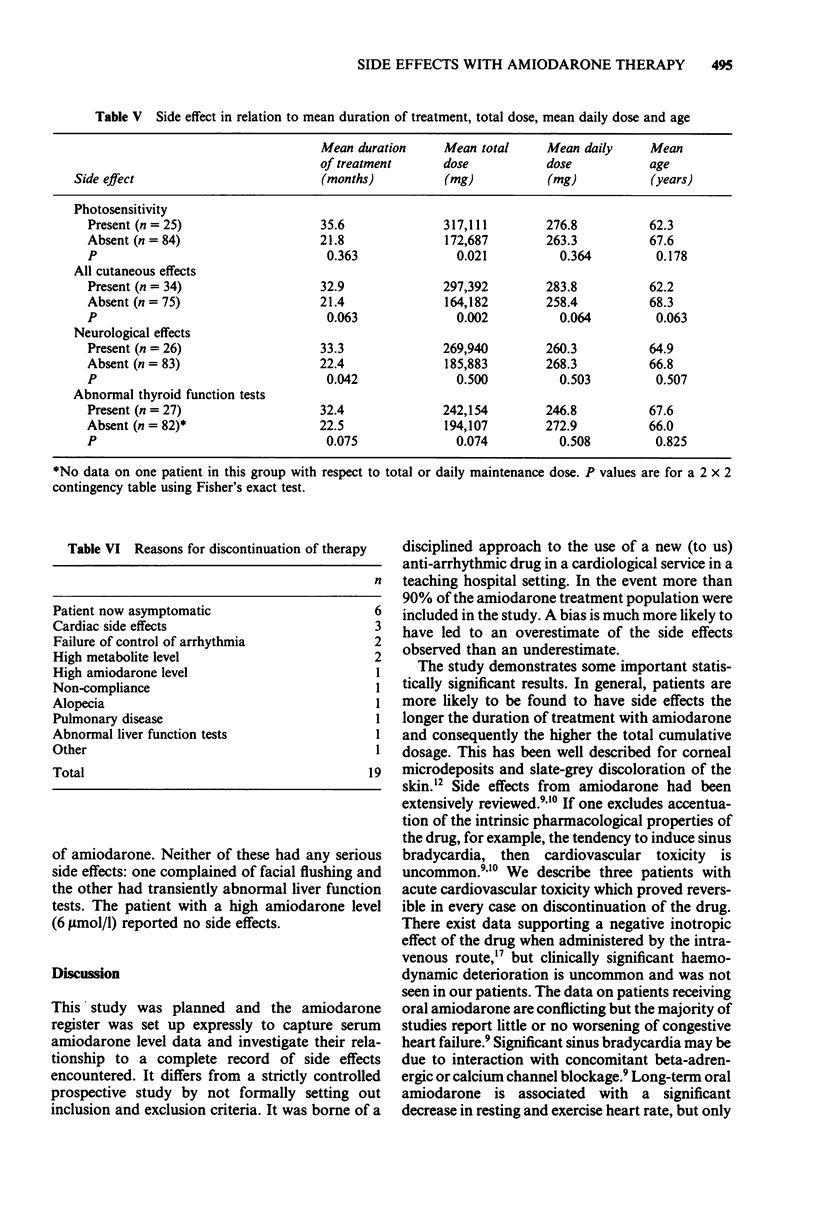
Amiodarone hydrochloride is increasingly being used in the treatment of ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias. Although a highly effective anti-arrhythmic agent, its use is restricted by the high incidence of side effects. To elucidate the value of monitoring serum level of both the parent drug and its active metabolite in predicting the occurrence of side effects, the investigators examined 109 patients from a register of patients treated with amiodarone for the prevalence of known side effects of the drug. The register contained over 90% of patients treated with amiodarone at the Leicester General Hospital during the period of the study. The findings suggest cutaneous side effects and abnormal thyroid function tests (without overt gland dysfunction) are more likely to occur with increasing duration of treatment and cumulative dosage. However, neither the serum amiodarone level nor the serum metabolite level had any predictive power for the occurrence of side effects. In view of this finding, it is recommended that close attention be paid to the continued clinical monitoring of side effects and that there is utility in measuring the serum amiodarone level in each patient to avoid the prescription of unnecessarily high doses. This is necessary not only to lessen the occurrence of cumulative dose-related side effects, but also because the variable but very long half-life of the drug leads to difficulties in relating spot drug levels to long-term effects.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Charness M. E., Morady F., Scheinman M. M. Frequent neurologic toxicity associated with amiodarone therapy. Neurology. 1984 May;34(5):669–671. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.5.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland J. G., Dargie H. J., Findlay I. N., Wilson J. T. Clinical, haemodynamic, and antiarrhythmic effects of long term treatment with amiodarone of patients in heart failure. Br Heart J. 1987 May;57(5):436–445. doi: 10.1136/hrt.57.5.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklyn J. A., Davis J. R., Gammage M. D., Littler W. A., Ramsden D. B., Sheppard M. C. Amiodarone and thyroid hormone action. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1985 Mar;22(3):257–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1985.tb03238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J., Heel R. C., Fitton A. Amiodarone. An overview of its pharmacological properties, and review of its therapeutic use in cardiac arrhythmias. Drugs. 1992 Jan;43(1):69–110. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199243010-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. L., Lerman B. B., Shipe J. R., Kaiser D. L., DiMarco J. P. Relation between amiodarone and desethylamiodarone plasma concentrations and electrophysiologic effects, efficacy and toxicity. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987 May;9(5):1148–1155. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L., McKenna W. J., Rowland E., Holt D. W., Storey G. C., Krikler D. M. Side effects of long-term amiodarone therapy. Circulation. 1983 Jan;67(1):45–51. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.67.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heger J. J., Prystowsky E. N., Jackman W. M., Naccarelli G. V., Warfel K. A., Rinkenberger R. L., Zipes D. P. Clinical efficacy and electrophysiology during long-term therapy for recurrent ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 1981 Sep 3;305(10):539–545. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198109033051002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt D. W., Tucker G. T., Jackson P. R., Storey G. C. Amiodarone pharmacokinetics. Am Heart J. 1983 Oct;106(4 Pt 2):840–847. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(83)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram D. V. Ocular effects in long-term amiodarone therapy. Am Heart J. 1983 Oct;106(4 Pt 2):902–905. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(83)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosinski E. J., Albin J. B., Young E., Lewis S. M., LeLand O. S., Jr Hemodynamic effects of intravenous amiodarone. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1984 Sep;4(3):565–570. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(84)80103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudenchuk P. J., Pierson D. J., Greene H. L., Graham E. L., Sears G. K., Trobaugh G. B. Prospective evaluation of amiodarone pulmonary toxicity. Chest. 1984 Oct;86(4):541–548. doi: 10.1378/chest.86.4.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latini R., Tognoni G., Kates R. E. Clinical pharmacokinetics of amiodarone. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1984 Mar-Apr;9(2):136–156. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198409020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchlinski F. E., Gansler T. S., Waxman H. L., Josephson M. E. Amiodarone pulmonary toxicity. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Dec;97(6):839–845. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-6-839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGovern B., Garan H., Kelly E., Ruskin J. N. Adverse reactions during treatment with amiodarone hydrochloride. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Jul 16;287(6386):175–180. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6386.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard D. A., Singh B. N., Hurley P. J. Effects of amiodarone on thyroid function in patients with ischaemic heart disease. Br Heart J. 1975 Aug;37(8):856–860. doi: 10.1136/hrt.37.8.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva E., Gerna M., Latini R., Giani P., Volpi A., Maggioni A. Pharmacokinetics of amiodarone in man. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):264–269. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198203000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotmensch H. H., Belhassen B. Amiodarone in the management of cardiac arrhythmias: current concepts. Med Clin North Am. 1988 Mar;72(2):321–358. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30773-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotmensch H. H., Belhassen B., Swanson B. N., Shoshani D., Spielman S. R., Greenspon A. J., Greenspan A. M., Vlasses P. H., Horowitz L. N. Steady-state serum amiodarone concentrations: relationships with antiarrhythmic efficacy and toxicity. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Oct;101(4):462–469. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-4-462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotmensch H. H., Liron M., Tupilski M., Laniado S. Possible association of pneumonitis with amiodarone therapy. Am Heart J. 1980 Sep;100(3):412–413. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(80)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland E., McKenna W. J., Krikler D. M. Amiodarone for the conversion of established atrial fibrillation and flutter. Br J Clin Pract Suppl. 1986 Apr;44:39–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh B. N., Nademanee K. Amiodarone and thyroid function: clinical implications during antiarrhythmic therapy. Am Heart J. 1983 Oct;106(4 Pt 2):857–869. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(83)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrobel T. R., Miller P. E., Mostow N. D., Rakita L. A general overview of amiodarone toxicity: its prevention, detection, and management. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1989 May-Jun;31(6):393–426. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(89)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. E., Camm A. J., Spurrell R. A. Clinical antiarrhythmic effects of amiodarone in patients with resistant paroxysmal tachycardias. Br Heart J. 1980 Jul;44(1):91–95. doi: 10.1136/hrt.44.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. S., Podrid P. J. Side effects from amiodarone. Am Heart J. 1991 Jan;121(1 Pt 1):158–171. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(91)90969-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary C. B., Slater D. N., Holt D. W., Storey G. C., MacDonald D. M. The pathogenesis of amiodarone-induced pigmentation and photosensitivity. Br J Dermatol. 1984 Apr;110(4):451–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1984.tb04660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


