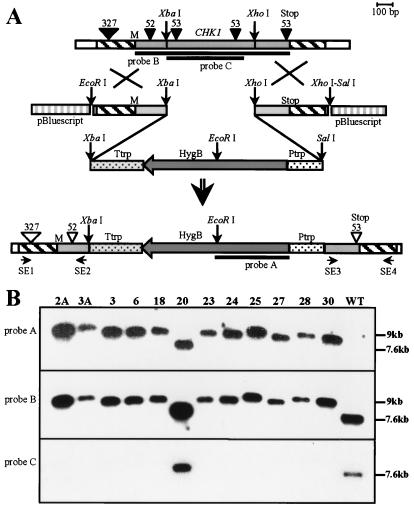
Figure 2.
Strategy for CHK1 gene disruption and analysis of transformants. (A) CHK1 replacement vector contains a 2.1-kb hygB resistance gene cassette. The 538-bp-long left flanking region includes the first 241 bp of CHK1 coding sequence, and the 501-bp-long right flanking region includes the last 205 bp of the CHK1 coding sequence. Homologous recombination through a double-crossover event results in the replacement of part of CHK1 with the hygB resistance cassette. (B) Southern analysis of hygB-resistant transformants. Genomic DNA was digested with SalI. Lanes 1–12 represent 12 different transformants (2A and 3A are MAT-1 and the others are MAT-2); lane 13 is wild type (MAT-2). The blot was sequentially hybridized with probes A, B, and C, which are indicated in A. The 7.6-kb band corresponds to the nondisrupted CHK1, and a 9-kb band results from hygB integration. All transformants except strain 20 show the pattern of hybridization expected for Δchk1 mutants resulting from double-crossover gene replacement; strain 20, the result of an ectopic integration event, retains the wild-type fragment hybridizing with probe C. Sizes and locations of introns are indicated by inverted triangles. Solid triangles indicate introns in the genomic sequence (GenBank accession no. AF178977), and open triangles indicate that these may or may not be present after recombination with the cDNA-derived vector sequences. The locations of primers SE1–4 used for amplifications in the flanking regions are indicated.