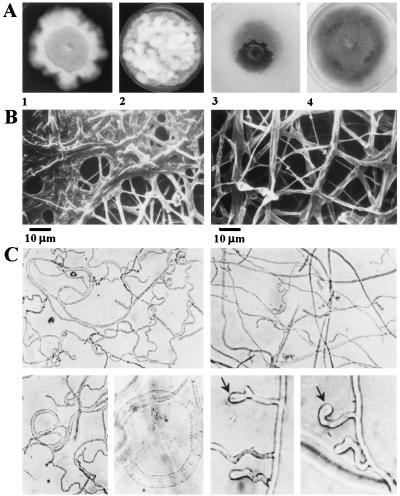
Figure 3.
Effects of targeted deletions at CHK1 on colony and hyphal development. (A) Colony morphology of Δchk1 mutants. (1 and 2) Colonies grown on CM. Plates were incubated at 30°C in the dark for 1 week. (3 and 4) Colonies grown on minimal medium. Plates were incubated at 25°C in UVA-enriched white light for 1 week. (1 and 3) chk1–3A and chk1–30, grown with hygB. (2 and 4) Wild-type controls. (B) Altered ultrastructural morphology of fungal colonies as a consequence of disruption of CHK1. Scanning electron micrographs show an apparent fusion or adhesion of hyphae in the central region of mutant colonies. (Left) chk1–30. (Right) WT. (C) Appressorium formation on a glass surface. (Left) chk1–30. (Right) Ectopic control, strain 20. Small appressoria appear as enlarged hyphal tips (arrows).