Abstract
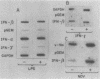
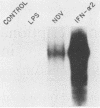
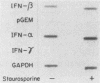
Low levels of beta interferon (IFN) mRNA are transcribed in freshly explanted murine peritoneal macrophages. Nuclear runoff transcription assays show that this "constitutive" IFN-beta-mRNA transcription does not increase in macrophages treated either with lipopolysaccharide or with IFN-gamma, which induce a marked accumulation of this mRNA and greatly increase IFN secretion. Therefore, these agents promote accumulation of IFN-beta mRNA by posttranscriptional mechanisms. The IFN-alpha 2 gene is also constitutively transcribed by macrophages, but the corresponding mRNA does not accumulate in lipopolysaccharide-treated cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. A., Cohen D. S., Wright S. D., Cohn Z. A. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides prime macrophages for enhanced release of arachidonic acid metabolites. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belardelli F., Gessani S., Proietti E., Locardi C., Borghi P., Watanabe Y., Kawade Y., Gresser I. Studies on the expression of spontaneous and induced interferons in mouse peritoneal macrophages by means of monoclonal antibodies to mouse interferons. J Gen Virol. 1987 Aug;68(Pt 8):2203–2212. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-8-2203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belardelli F., Vignaux F., Proietti E., Gresser I. Injection of mice with antibody to interferon renders peritoneal macrophages permissive for vesicular stomatitis virus and encephalomyocarditis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):602–606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Piechaczyk M., Audigier Y., El Sabouty S., Cathala G., Marty L., Fort P., Blanchard J. M., Jeanteur P. Characterization of the transcription products of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate-dehydrogenase gene in HeLa cells. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 3;145(2):299–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessani S., Belardelli F., Borghi P., Boraschi D., Gresser I. Correlation between the lipopolysaccharide response of mice and the capacity of mouse peritoneal cells to transfer an antiviral state. Role of endogenous interferon. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1991–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessani S., Belardelli F., Pecorelli A., Puddu P., Baglioni C. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide and gamma interferon induce transcription of beta interferon mRNA and interferon secretion in murine macrophages. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2785–2789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2785-2789.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessani S., McCandless S., Baglioni C. The glucocorticoid dexamethasone inhibits synthesis of interferon by decreasing the level of its mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7454–7457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression of murine immune interferon cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Vignaux F., Belardelli F., Tovey M. G., Maunoury M. T. Injection of mice with antibody to mouse interferon alpha/beta decreases the level of 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetase in peritoneal macrophages. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):221–227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.221-227.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A., Becton D. L., Somers S. D., Gray P. W., Adams D. O. Interferon-gamma modulates protein kinase C activity in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1378–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Sokawa Y., Watanabe Y., Kawade Y., Ohno S., Takaoka C., Taniguchi T. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for mouse interferon-beta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9522–9529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoss-Homfeld A., Zwarthoff E. C., Zawatzky R. Cell type specific expression and regulation of murine interferon alpha and beta genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):539–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90566-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proietti E., Gessani S., Belardelli F., Gresser I. Mouse peritoneal cells confer an antiviral state on mouse cell monolayers: role of interferon. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):456–463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.456-463.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Two levels of regulation of beta-interferon gene expression in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3923–3927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. D., Boll W., Taira H., Mantei N., Lengyel P., Weissmann C. Structure and expression of cloned murine IFN-alpha genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):555–573. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Fertsch D. Macrophages from endotoxin-hyporesponsive (Lpsd) C3H/HeJ mice are permissive for vesicular stomatitis virus because of reduced levels of endogenous interferon: possible mechanism for natural resistance to virus infection. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):812–818. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.812-818.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamato K., el-Hajjaoui Z., Koeffler H. P. Regulation of levels of IL-1 mRNA in human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jun;139(3):610–616. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zullo J. N., Cochran B. H., Huang A. S., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor and double-stranded ribonucleic acids stimulate expression of the same genes in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]