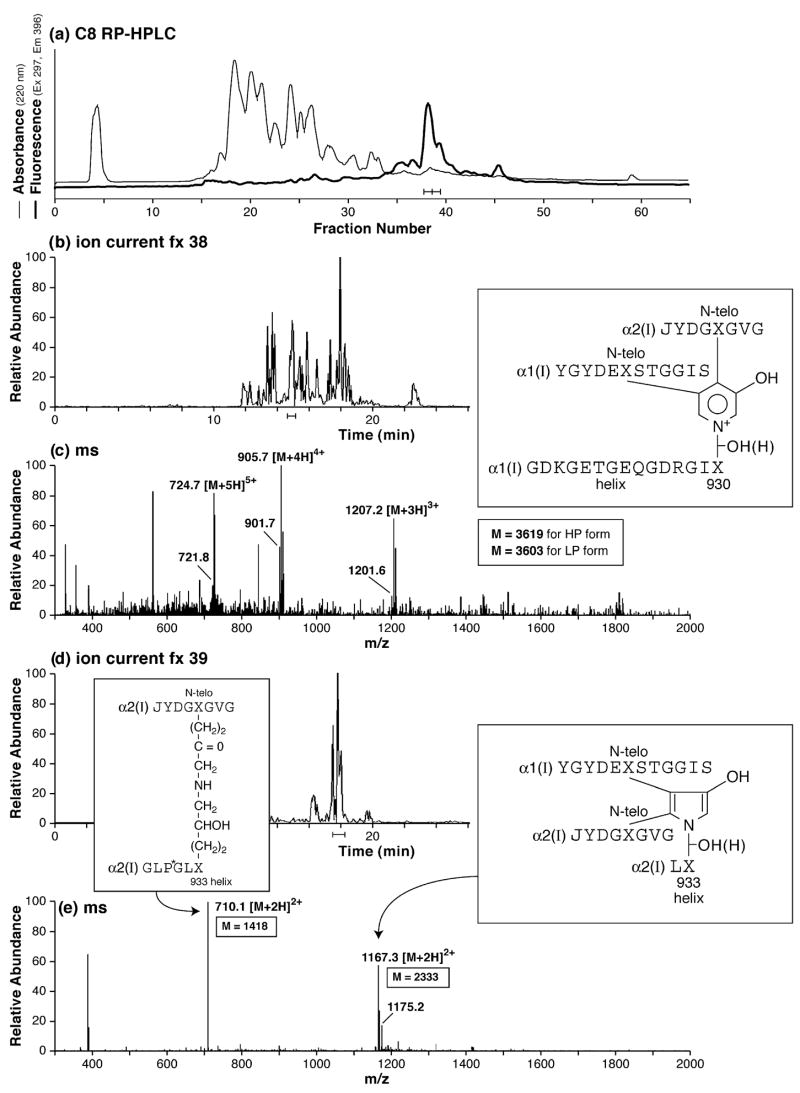
Fig. 4.
RP-HPLC resolution and mass spectrometric structural identification of cross-linked peptides from human bone collagen digested by cathepsin K in vitro. (a) RP-HPLC and detection by fluorescence of trivalent pyridinoline-containing peptides from the cathepsin K digest. (b and c) LC/MS resolution and detection of a major pyridinoline-containing peptide from fraction 38. The HP and LP forms of the same peptide are resolved in the mass spectrum as ions that differ by 16 mass units (= oxygen atom), e.g., 905.7 and 901.7 for the 4+ charge state. (d and e) LC/MS resolution and detection of a major pyrrole-containing cross-linked peptide from fraction 39 of the HPLC profile. The predominant 2+ charge state of the pyrrole structure is a useful distinguishing feature from the predominant 3+ charge of the equivalent peptide in which the cross-link is a pyridinoline residue (latter not shown).