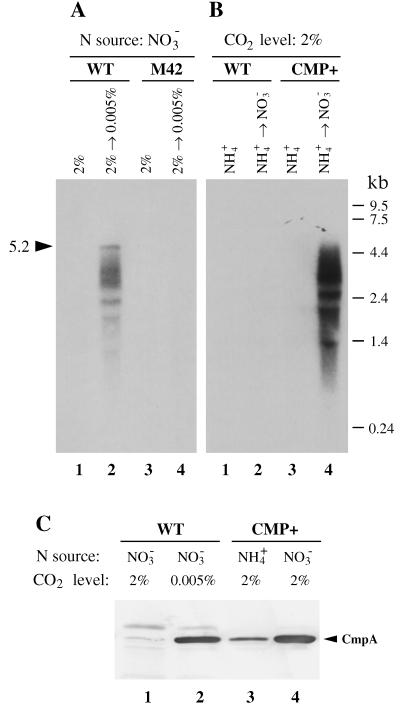
Figure 2.
(A) Northern hybridization analysis of total RNA from Synechococcus, showing the effects of CO2 conditions on expression of the cmp operon. Synechococcus cells were grown with NO3− under high-CO2 conditions (2% CO2 in air) and transferred to low-CO2 conditions (0.005% CO2 in air). RNA samples (10 μg per lane) from WT (lanes 1 and 2) and the M42 mutant (lanes 3 and 4), extracted before (lanes 1 and 3) and 30 min after (lanes 2 and 4) the transfer, were denatured with formamide, separated on a 1.2% agarose-formaldehyde gel, transferred to a positive-charged nylon membrane (Hybond N+, Amersham), and hybridized with a 32P-labeled cmpC-specific probe. (B) Northern hybridization analysis of total RNA, showing the nitrogen-regulated expression of the cmp gene cluster under high CO2 in the CMP+ mutant. Synechococcus cells were grown with NH4+ and transferred to NO3−-containing medium under high-CO2 conditions. RNA samples (10 μg per lane) from WT (lanes 1 and 2) and CMP+ (lanes 3 and 4), extracted before (lanes 1 and 3) and 30 min after (lanes 2 and 4) the transfer, were analyzed as in A. (C) Immunoblotting analysis of CmpA in the plasma membrane of Synechococcus grown under constant C and nitrogen conditions. Plasma membrane samples from WT cells grown under high CO2 (lane 1) and low CO2 (lane 2) conditions in NO3−-containing medium and those from the CMP+ cells grown under high-CO2 conditions in NH4+- (lane 3) and NO3−- (lane 4) containing media were compared. Membrane proteins (5 μg per sample) were solubilized with SDS, fractionated by SDS/PAGE (10% gel), and electrotransferred to poly(vinylidene difluoride) membrane for immunostaining.